The two spring couplings on the motor shaft, the flexible couplings between sections of the drive shaft,
and the tone wheel spring couplings all contribute to absorbing variations in motor speed. The
synchronous motor does not deliver absolutely steady power, but rather operates with a series of
pulsations, one with each half cycle. If the tone wheels were rigidly coupled to the motor, this slight
irregularity would carry extra frequencies into each tone wheel. In addition, "hunting" is suppressed by
the resilient couplings and inertia members of the synchronous motor proper.
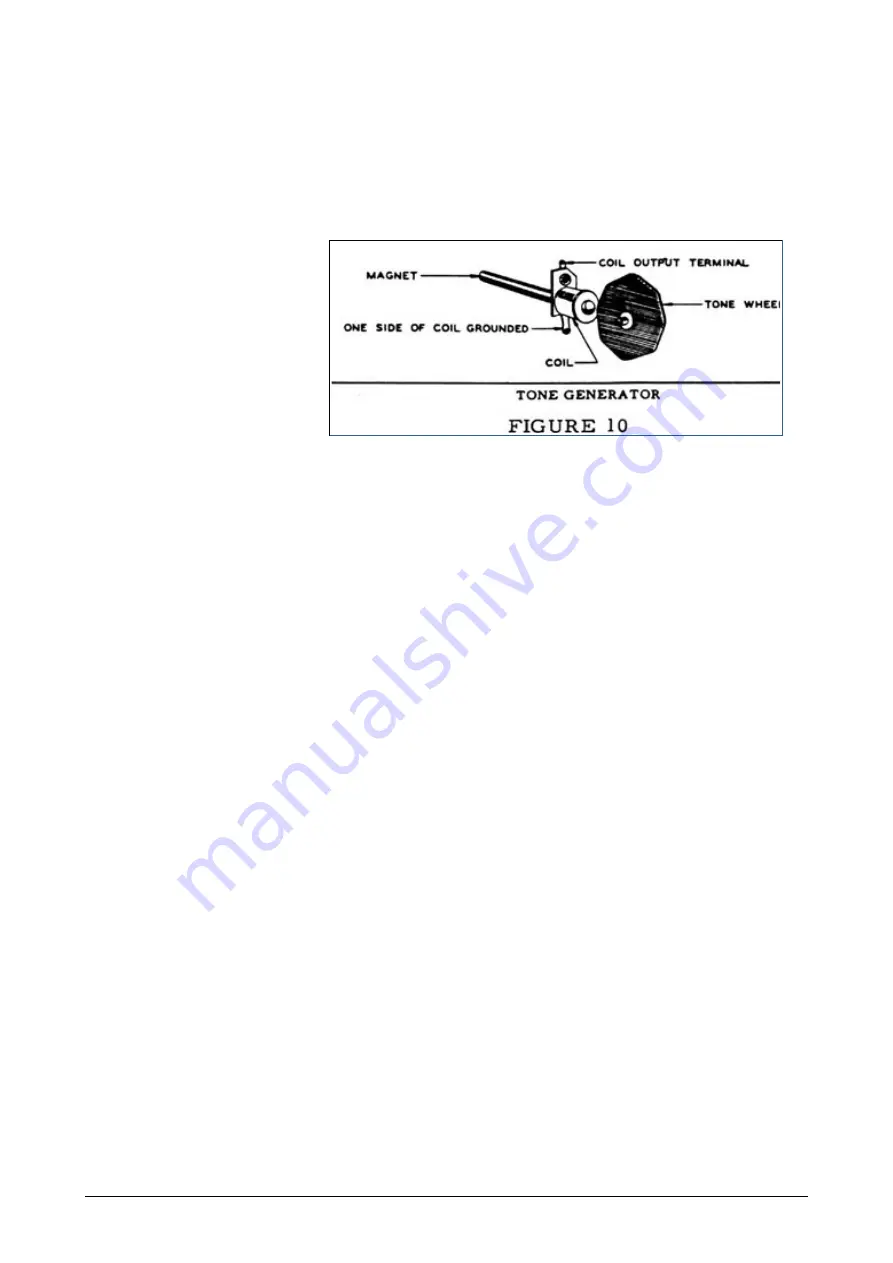
Associated with each tone wheel is a magnetized rod about 1/4 of an inch in diameter and 4 inches in
length, with a coil of wire wound near one end (See
Figure 10
).
The tip of the magnet at the coil end is ground to a sharp edge and mounted near the edge of the tone
wheel. Each time a tooth passes this rod it causes a change in the magnetic field, which induces a
small voltage in the coil, the frequency being determined by the number of teeth and the wheel speed.
Small coils are used on the higher frequency magnets and larger coils on the lower frequencies. It is
found that large pole pieces are needed on the low frequency magnets to give proper output, but it is
necessary to use smaller ones on the high frequencies to prevent excessive iron losses.
Some of the coils have copper rings mounted on them for the purpose of reducing harmonics. As these
are used only on fairly low frequency coils, the eddy current loss in such a ring is small for the
fundamental frequency of that coil, but high for its harmonics. This has the effect of reducing the relative
intensities of any harmonics which may be produced by irregularites in the tone wheels. The wheels are
cut so to give as nearly a sine wave as possible, but the generated voltage seldom reaches that ideal
condition, since even a slight change in the air gap will change the wave form.
9
tuttotastiere.com










































