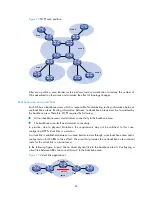
92
•
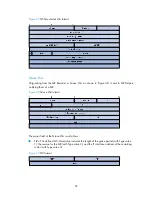
M (More): The More bit, which is set to 0 if the packet is the last packet of DD packets, and
set to 1 if more DD Packets are to follow.
•
MS: The Master/Subordinate bit. When set to 1, it indicates that the router is the master
during the database exchange process. Otherwise, the router is the subordinate.
•
DD sequence number: Used to sequence the collection of database description packets for
ensuring reliability and intactness of DD packets between the master and subordinate. The
initial value is set by the master. The DD sequence number then increments until the complete
database description has been sent.
LSR packet
After exchanging DD packets, any two routers know which LSAs of the peer routers are missing
from the local LSDBs. In this case, they send LSR packets, requesting the missing LSAs. The
packets contain the brief of the missing LSAs.
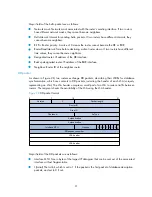
Figure 29
LSR packet format
Major fields of the LSR packets are as follows:
•
LS type: Type number of the LSA to be requested. Type 1, for example, indicates the Router
LSA.
•
Link state ID: Determined by LSA type.
•
Advertising router: ID of the router that sent the LSA.
LSU packet
LSU packets are used to send the requested LSAs to peers, and each packet carries a collection of
LSAs.
Summary of Contents for S9500E Series
Page 435: ...435 ...