19
5. The difference between the thermometer reading and
pressure to temperature conversion is the amount of
subcooling.
Subcooling Formula = Sat. Liquid Temp. - Liquid Line
Temp.
EXAMPLE:
a. Liquid Line Pressure = 417
b. Corresponding Temp. °F. = 120°
c. Thermometer on Liquid line = 109°F.
To obtain the amount of subcooling, subtract 109°F from
120°F.
The difference is 11° subcooling. See the specification
sheet or technical information manual for the design
subcooling range for your unit.
See R410A Pressure vs. Temperature chart.
Compressor Protection Devices
The compressor includes components which are designed
to protect the compressor against abnormal operating
conditions.
Refrigerant Charge Check (Units with Fixed Orifice
Devices)
After completing airflow measurements and adjustments
the unit’s refrigerant charge must be checked. The unit
comes factory charged, but this charge is based on 325
CFM per ton and minimum ESP per AHRI test conditions
(generally between .15 -.28 ESP). When air quantity or
ESP is different than above, the refrigerant charge must be
adjusted to the proper amount. All package units with fixed
orifice devices are charged using the super heat method at
the compressor suction line.
After superheat is adjusted it is recommended to check unit
sub-cooling at the condenser coil liquid line out. For charge
adjustments, see superheat and subcooling charts shown
for each model.
MAINTENANCE
Have the gas heating section of the unit checked at least
once a year before the heating season begins, to be sure
that the combustion air inlet and flue outlet hoods are
not blocked by debris, which would prevent adequate
combustion air and a properly operating vent system.
Filter Replacement or Cleaning
A return air filter is not supplied with this unit; however,
there must be a means of filtering all of the return air. The
filter(s) may be located in the return air duct(s), or return
air filter grille(s). Consult with your installing dealer for the
actual location of the return air filter(s) for your unit.
Dirty filters are the most common cause of inadequate
heating or cooling performance. Filter inspection should be
made at least every two months; more often if necessary
because of local conditions and usage.
Dirty throwaway filters should be discarded and replaced
with a new, clean filter. Dirty permanent filters should be
washed with water, thoroughly dried and sprayed with a
filter adhesive before being reinstalled. (Filter adhesives
may be found at many hardware stores.) Permanent filters
should last several years. However, should one become
torn or uncleanable, it should be replaced.
Cabinet Finish Maintenance
Use a fine grade automotive wax on the cabinet finish to
maintain the finish’s original high luster. This is especially
important in installations with extended periods of direct
sunlight.
Clean Outside Coil (Qualified Servicer Only)
The coil with the outside air flowing over it should be
inspected annually and cleaned as frequently as necessary
to keep the finned areas free of lint, hair and debris.
Condenser, Evaporator, and Induced Draft Motors
Bearings on the air circulating blower motor, condenser
motor and the combustion fan motor are permanently
lubricated. No additional oiling is required.
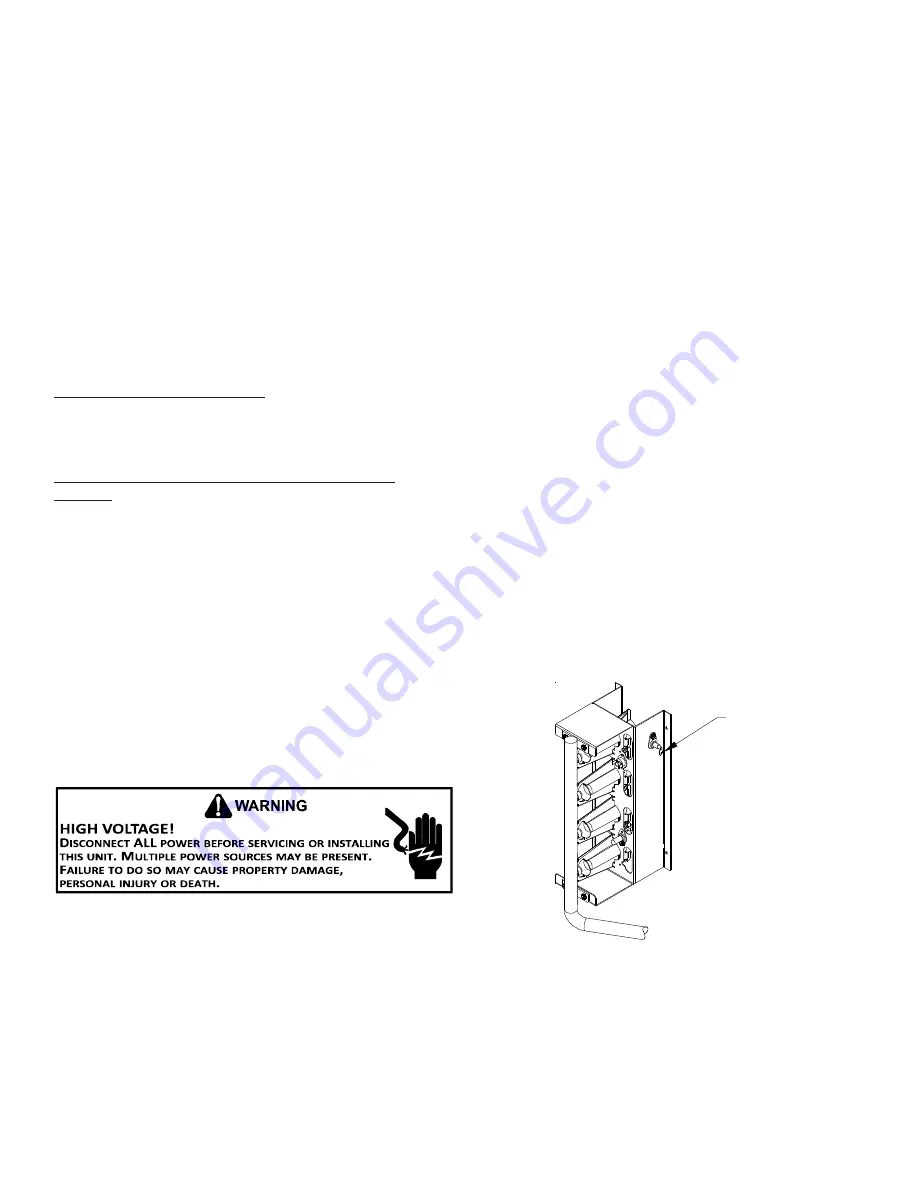
Flame Sensor (Qualified Servicer Only)
A drop in the flame current can be caused by a nearly
invisible coating on the flame sensor. This coating, created
by the fuel or combustion air supply, can be removed by
carefully cleaning the flame sensor with steel wool.
NOTE:
After cleaning, the microamp signal should be
stable and in the range of 4 - 6 microamps DC.
Flame
Sensor
Flame Sensor
Flue Passages (Qualified Servicer Only)
At the start of each heating season, inspect and, if
necessary, clean the unit flue passage.
1. Shut off electric power and gas supply to the unit.
2. Remove burner assembly by disconnecting the gas
line and removing the manifold bracket from the
partition panel.
Summary of Contents for APD 14 M Series
Page 23: ...23 UNIT DIMENSIONS...






































