GEK-113188A
MIGII Digital Protection for Electrical Machines
A-7
APPENDIX A
A.6 MIGII THERMAL CURVES
A
A.6MIGII THERMAL CURVES
The equation for the temperature given before was:
MIGII
uses an equation, in which the tripping time is a function of the current flowing through the protected element, thus
eliminating all references to the temperatures. The heating time constant
τ
in MIGII
is designated as
τ
1.
By means of the keypad (or EnerVista MIIPC program), a tap/pickup current must be set in the relay. If
the current is greater than the programmed tap current, the thermal protection will trip after a
period of time given by the following equation:
Where:
t Tripping
time.
τ
1
Heating time constant.
I’
I / I
tap
I
Current through the element.
I
tap
Programmed tap/pickup current in the relay.
This equation can only be applied if the relay starts from a thermal zero status, that is, from a condition at which a current
I = 0 was flowing through it. If the relay had stabilised at a condition at which a given current was flowing through it, the
value of which is smaller than the rated current, and at a given moment the current increases up to a value greater than
the rated current, the tripping time from the moment the increase takes place is given by the equation:
Where:
I
e
Ime / I
tap
Ime
Current at which the protected element had stabilised.
I
tap
Programmed tap current.
and the rest of the symbols have the same meaning as in the previous equation.
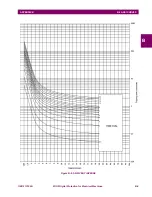
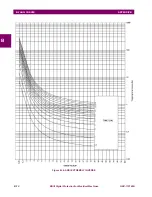
In the curves, the “Thermal Equivalent Current” is represented by the letter Ieq, and this is the value that the relay shows
corresponding to the thermal image of the protected element. The relay is running the thermal image for the three
phases, but only the greater value is shown in the display, as it is the one that will cause the trip.
When the protected element cools down, the time constant (Cooling Time Constant) may be different than the heating
time constant. For motors and generators applications, the heat transfer between the machine and the ambient, it
different depending on if the machine is stopped or if it is spinning. To detect this stopped motor or generator (or in
general, protected element disconnected), MIGII relay uses an internal current level detector, fixed to 15% In. If the
current flowing through the element is lower than this value, the relay will consider that the element is disconnected and
will use in its algorithms and equations a different “Cooling” time constant
τ
2. This time constant is a setting in the relay,
and its range is from 1 to 6 times the heating time constant
τ
1. If the current is greater than 15% In, the element will be
considered to be connected (spinning), and then, the cooling time constant will be
τ
1.
Summary of Contents for Multilin MIGII
Page 2: ......