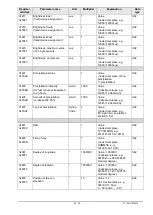
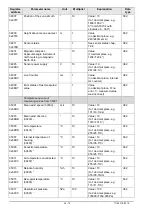
10 - 70
71130/11E/0318
Moving averaging
of the wind velocity and wind direction acc. to the
WMO- recommendations
:
The wind data can be averaged moving over a time span of up to 10 minutes on a base of
100 millisecond values. This averaging is calculated according the recommendation of the WMO as
the FIFO-method. That means, that all data are kept in the memory up to the end of the averaging
period. Thus, a data outlier can be identified as such, and - contrary to a first-order averaging
–
does not lead to a settling of its influence for a longer period.
3.1.2 Measuring principle: Acoustic virtual temperature
The thermodynamic interrelationship between the propagation speed of sound and the absolute air
temperature is defined by a root function. The speed of sound is also more or less independent of
the air pressure and only depends on the absolute air humidity to an insignificant extent.
This physical relationship between the speed of sound and temperature can be used to measure
the temperature of the air as long as its chemical composition is known and remains constant. The
levels of gases in the atmosphere are constant and, with the exception of the content of water
vapour, vary by no more than a few 100ppm (CO
2
) even over lengthy periods.
The determination of gas temperature via its speed of sound is performed directly from
measurement of its physical properties without the indirect step of thermal coupling of this gas to a
sensor, which would otherwise be necessary.
Note:
The acoustic-virtual temperature is the air temperature which refers to dry air
without any water vapour. It is detected by sonic logging of acoustic pulses .
The acoustic temperature is not suitable for the exact measurement of air
temperature. It serves exclusively for the verification of the acquired wind
measuring values.