Requirements for the connecting cable
Characteristics
–
Encoder cable for servo drives, shielded
–
Optical shield cover
>
85 %
–
Separately twisted signal pairs
–
Recommended design: (4 x (2 x 0.25 mm
2
))
1)
Max. cable length
100 m
1)
1) In the case of encoders with no compensation for voltage drops or in the case of very long cables, thicker
supply cables may be required.
Tab. 20: Requirements for the connecting cable
Shield support requirements
Connecting the encoder cable shield
1. On the device side, connect the encoder cable shield to the plug housing.
2. On the motor side, connect the encoder cable shield to the encoder or
encoder plug.
7.8.4
[X3], encoder interface 2
The encoder interface [X3] is located on the front side of the device. The encoder
interface [X3] primarily serves to connect a second position encoder to the axis
(e.g. to enable precise positioning control for the axis or as a redundant meas-
uring system for safe motion monitoring).
Supported standards/protocols
Supported encoders
Digital incremental encoders with square-wave
signals and with RS422-compatible signal out-
puts (differential A, B, N signals)
ROD 426 or compatible
ELGO LMIX 22
Analogue SIN/COS incremental encoders with
differential analogue signals with 1 V
ss
HEIDENHAIN LS 187/LS 487 (20 µm signal
period) or compatible
Tab. 21: Standards and protocols supported by the encoder interface [X3]
[X3] is designed to be electrically compatible with [X2] but does not support all
encoders and functions like [X2].
7.8.5
[X10], SYNC IN/OUT
The interface [X10] is located on the front of the device. The interface [X10]
permits master-slave coupling. In the master-slave coupling, the axes of several
devices (slave axes) are synchronised via a device (master axis). The SYNC inter-
face can be configured for different functions and can be used as follows:
Possible functions
Description
Incremental encoder output
Output of a master axis that emulates encoder
signals (encoder emulation)
Incremental encoder input
Input of a slave axis for receiving the encoder
signals of a master axis
Tab. 22: Possible functions of the connection [X10]
Requirements for the connecting cable
Characteristics
–
Encoder cable for servo drives, shielded
–
Optical shield cover
>
85%
–
Separately twisted signal pairs
–
recommended design: (4 x (2 x 0.25 mm
2
))
Max. cable length
3 m
Tab. 23: Requirements for the connecting cable
Shield support requirements
Connect the connecting cable shield to the plug housings on both sides.
Possible connections
Connection possibilities
Description
Direct connection of 2 devices
Two devices can be connected directly with a
patch cable (point-to-point connection).
Recommendation: use Cat 5e category patch
cable; maximum length: 25 cm
Connection of multiple devices via RJ45 T
adapter and patch cables
A maximum of 16 devices may be connected.
Recommendation: use T adapter and Cat 5e cat-
egory patch cables; maximum length per cable:
25 cm
Connection of multiple devices via patch
cables and a connector box (accessories
A maximum of 16 devices may be connected.
Recommendation: use Cat 5e category patch
cables; maximum length per cable: 100 cm
Tab. 24: Connection possibilities
7.8.6
[X18], Standard Ethernet
The interface [X18] is located on the front of the device. The following can be
performed via the interface [X18] using the commissioning software:
–
Diagnostics
–
Parameterisation
–
Control
–
Firmware update
The interface is designed to conform to the standard IEEE 802.3. The interface
is electrically isolated and intended for use with limited cable lengths
Requirements for the connecting cable. For this reason, the insulation coordina-
tion approach differs from IEEE 802.3 and must conform instead to the applicable
product standard IEC 61800-5-1.
Requirements for the connecting cable
Characteristics
CAT 5, patch cable, double shielded
Max. cable length
30 m
Tab. 25: Requirements for the connecting cable
The following connections are possible via the Ethernet interface:
Connections
Description
Point-to-point connection
The device is connected directly to the PC via an
Ethernet cable.
Network connection
The device is connected to an Ethernet network.
Tab. 26: Options for connection
The device supports the following methods of IP configuration (based on IPv4):
Methods
Description
Obtain IP address automatically (DHCP client)
The device obtains its IP configuration from a
DHCP server in your network. This method is
suitable for networks in which a DHCP server
already exists.
Fixed IP configuration
The device uses a fixed IP configuration.
The IP configuration of the device can be perma-
nently assigned manually. However, the device
can only be addressed if the assigned IP configu-
ration matches the IP configuration of the PC.
Factory setting: 192.168.0.1
Tab. 27: Options for IP configuration
7.8.7
[X19], Real-time Ethernet (RTE) port 1 and port 2
The interface [X19] is located on the top of the device. The interface [X19] permits
RTE communication. The following protocols are supported by the interface [X19],
depending on the product design:
Product variant
Supported protocol
CMMT-AS-...-EC
EtherCAT
CMMT-AS-...-EP
EtherNet/IP
CMMT-AS-...-PN
PROFINET
Tab. 28: Supported protocol
The physical level of the interface fulfils the requirements according to IEEE 802.3.
The interface is electrically isolated and intended for use with limited cable
lengths
Tab. 29 Requirements for the connecting cable.
The interface [X19] offers 2 ports.
–
Port 1, labelled on the device with [X19, XF1 IN]
–
Port 2, labelled on the device with [X19, XF2 OUT]
2 LEDs are integrated into each of the two RJ45 bushings. The behaviour of the
LEDs depends on the bus protocol. Use is not always made of both LEDs.
Requirements for the connecting cable
Characteristics
CAT 5, patch cable, double shielded
Max. cable length
30 m
Tab. 29: Requirements for the connecting cable
7.9
Motor connection
7.9.1
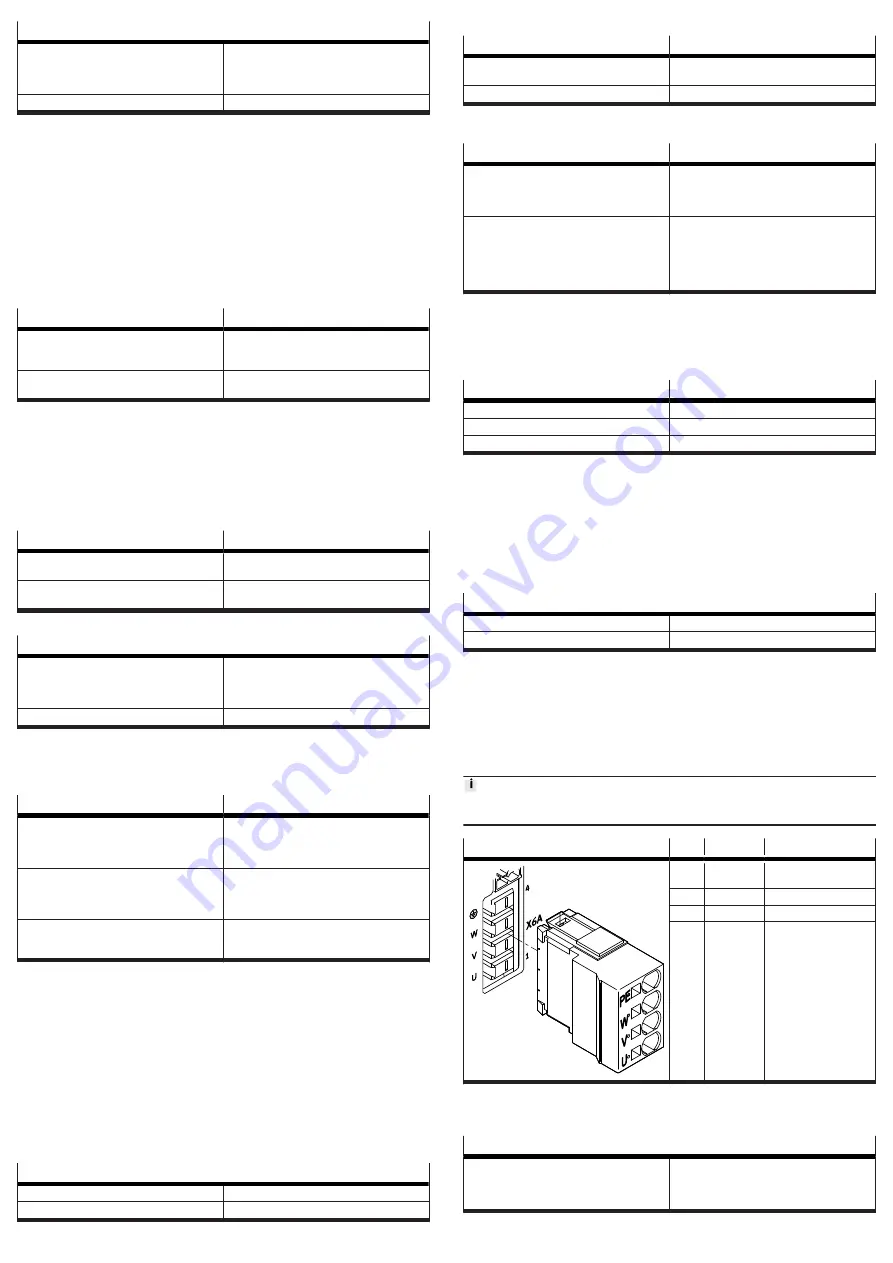
[X6A], motor phase connection
The connection [X6A] is located on the front of the device. The following connec-
tions to the motor are established via the connection [X6A]:
–
Motor phases U, V, W
–
PE connection
Incorrect circuitry of PE and motor phases results in a device defect, jerking or
uncontrolled start-up of the motor when the power supply is switched on.
[X6A]
Pin
Function
Description
4
PE
Protective earthing,
motor
3
W
third motor phase
2
V
second motor phase
1
U
first motor phase
Tab. 30: Motor phase connection
The cable shield of the motor cable must be placed on the support surface on the
bottom front of the housing and the motor cable fastened with the shield clamp.
Requirements for the connecting cable
Wires and shielding
–
4 power wires, shielded
–
Extra optional wires, e.g. for the holding brake
(shielded separately) and the motor tempera-
ture sensor (shielded separately)
















