EPSON Stylus COLOR 880
Revision A
Operating Principles
Electrical Circuit Operating Principles
44
1.
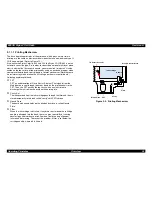
Regardless of the state of the power switch (On or OFF), the voltage is
always applied to the primary side of the power supply board from the
moment or at the state that AC-plug is plugged in. At this time, F1 plays a
role of preventing AC100V from coming into the F1.
L1 also prevents high harmonic wave noise generated in the RC circuit
filter which consists of C1,C2 from going out, and eliminates the noise from
outside here.
2) The AC is full-wave rectified by the diode bridge DB1, and converted to
x AC in voltage by the smoothing electrolytic capacitor C11.
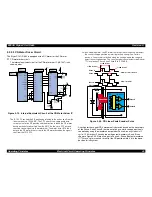
3) The pressured up direct current turns Q1 on through the starting resistor
R31 and starts the primary side of the circuit.
4) When the primary side is On, the energy (current) led by the
electromagnetic induction through the trans (T1) does not flow to the
secondary side since the diode (D51) on the secondary side is installed in
the opposite direction.
5) When the energy which is charged in the trans is reaching the saturated
state, the voltage which makes Q1 on becomes weak gradually. At the
point that this voltage drops at the certain voltage, C13 absorbs the current
in the opposite direction and Q1 is quickly shut off by the resulting sharp
drop.
6) When the primary side is turned off, the energy charged in the T1 is
opened according to the diode(D51) direction which is installed on the
secondary side. Basically, 42 V DC is output by these circuit operations
and the number of T1 spiral coil.
7) +5VDC is generated by pressured down this +42VDC as power supply.
IC51 pressures down the +42VDC and generates p5VDC by
chopping off the output, forming the standard santooth wave form by the
outer RC integration circuit.
The C378PSB/PSE board has the various control circuits to stop voltage
output if a malfunction occurs on the power supply board or the main board or
while the printer mechanism is on duty. Following explains each control and
protection circuit.
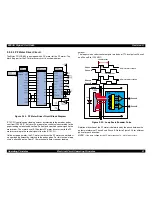
+42V Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit:
The output level of the +42V line is monitored by a detection circuit
composed of the seven Zener diodes. This circuit prevents the voltage
from dropping for a constant level of the output voltage.
+5V line over voltage protection circuit:
This protection circuit is in the same line as the +42V over voltage
protection circuit is located. The output voltage level of the +5V line is
monitored by a Zener diode. This circuit shuts down the +5V line forcefully
when the voltage level e9V.
+42VDC line drop limitation circuit:
This protection circuit is in the same line as +42V over voltage protection
circuit is located. The output voltage level of the +42V line is monitored by
a Zener diode. This circuit shuts down the +42V line forcefully when the
voltage level drops to +36V.
+42VDC line over voltage circuit:
This circuit is in the same line as +5V line over voltage protection circuit is
located. The output level is monitored by two Zener diodes. If the voltage
level e48VDC, this circuit shuts down the +42V line forcefully.
+5V line constant voltage/constant current control circuit:
The output current is monitored by the +5VDC generation switching control
IC (IC51), which also monitors the output voltage. This information is input
to the internal comparator and stab5V line. The operations of the
secondary side switch are explained below.
When the power is turned on, Q1 repeats on/off automatically along
with the increase and decrease of energy on the trans coil at the
primary side. While the power is on, the PSC signal is input to the
power supply board from the C378MAIN board.
This signal turns Q84 on and it becomes possible to discharge energy
between the terminals 8 and 9 of T1. At this time, even if the power is
turned off, the electrolytic capacitor keeps Q84 on for a while, and by
this electrolytic capacitor, voltage output is held at least 30 seconds.
This time helps the printer to complete a power-off operation.
2
Summary of Contents for Stylus Color 880
Page 9: ...C H A P T E R 1 PRODUCTDESCRIPTION ...
Page 30: ...C H A P T E R 2 OPERATINGPRINCIPLES ...
Page 55: ...C H A P T E R 3 TROUBLESHOOTING ...
Page 76: ...C H A P T E R 4 DISASSEMBLYANDASSEMBLY ...
Page 116: ...C H A P T E R 5 ADJUSTMENT ...
Page 142: ...C H A P T E R 6 MAINTENANCE ...
Page 152: ...7 APPENDIX C H A P T E R ...
Page 177: ......
Page 178: ......
Page 179: ......