Operation Section
-55-
Electronic Controlled Spark-Ignition Engines
G643E Engine
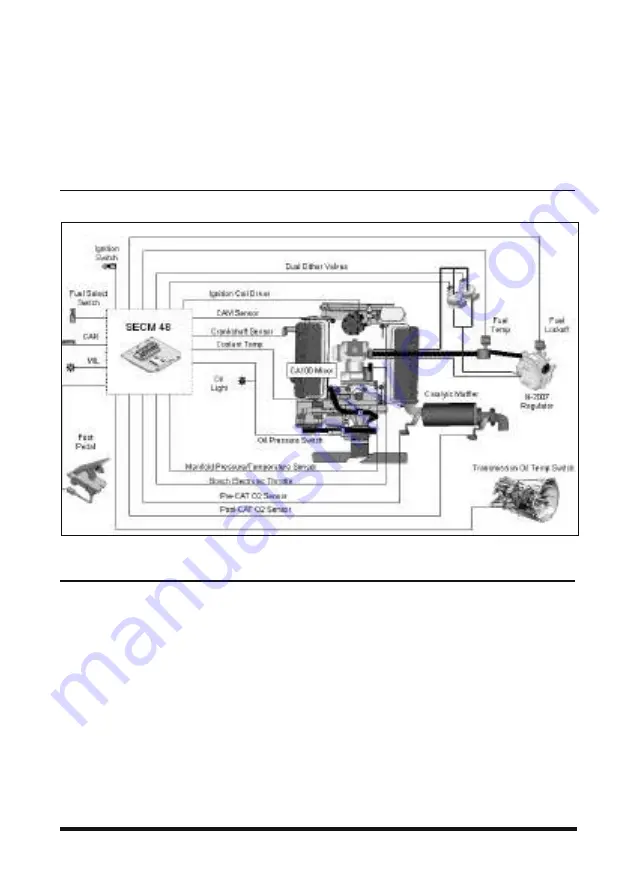
EMS (Engine management system) of G643E engine is
a closed loop system utilizing a catalytic muffler to
reduce the emission level in the exhaust gas. In order to
obtain maximum effect from the catalyst, an accurate
control of the air fuel ratio is required. A small engine
control module (SECM) uses two heated exhaust gas
oxygen sensors (HEGO) in the exhaust system to
monitor exhaust gas content. One HEGO is installed in
front of the catalytic muffler and one is installed after the
catalytic muffler.
The SECM makes any necessary corrections to the air
fuel ratio by controlling the inlet fuel pressure to the
air/fuel mixer by modulating the dual fuel trim valves
(FTV) connected to the regulator. Reducing the fuel
pressure leans the air/fuel mixture and increasing the
fuel pressure enriches the air/fuel mixture. To calculate
any necessary corrections to the air fuel ratio, the SECM
uses a number of different sensors to gain information
about the engine’s performance. Engine speed is
monitored by the SECM through a variable reluctance
(VR) or Hall Effect sensor. Intake manifold air
temperature and absolute pressure are monitored with a
TMAP sensor. MI-07 is a drive-by-wire (DBW) system
connecting the accelerator pedal to the electronic
throttle through the electrical harness; mechanical
cables are not used. A throttle position sensor (TPS)
monitors throttle position in relation to the accelerator
pedal position sensor (APP) command. Even engine
coolant temperature and adequate oil pressure are
monitored by the SECM. The SECM controller has full
adaptive learning capabilities, allowing it to adapt control
function as operating conditions change. Factors such
as ambient temperature, fuel variations, ignition
component wear, clogged air filter, and other operating
variables are compensated..
EMS schematic of G643E LP engine
https://www.forkliftpdfmanuals.com/
















































