3.
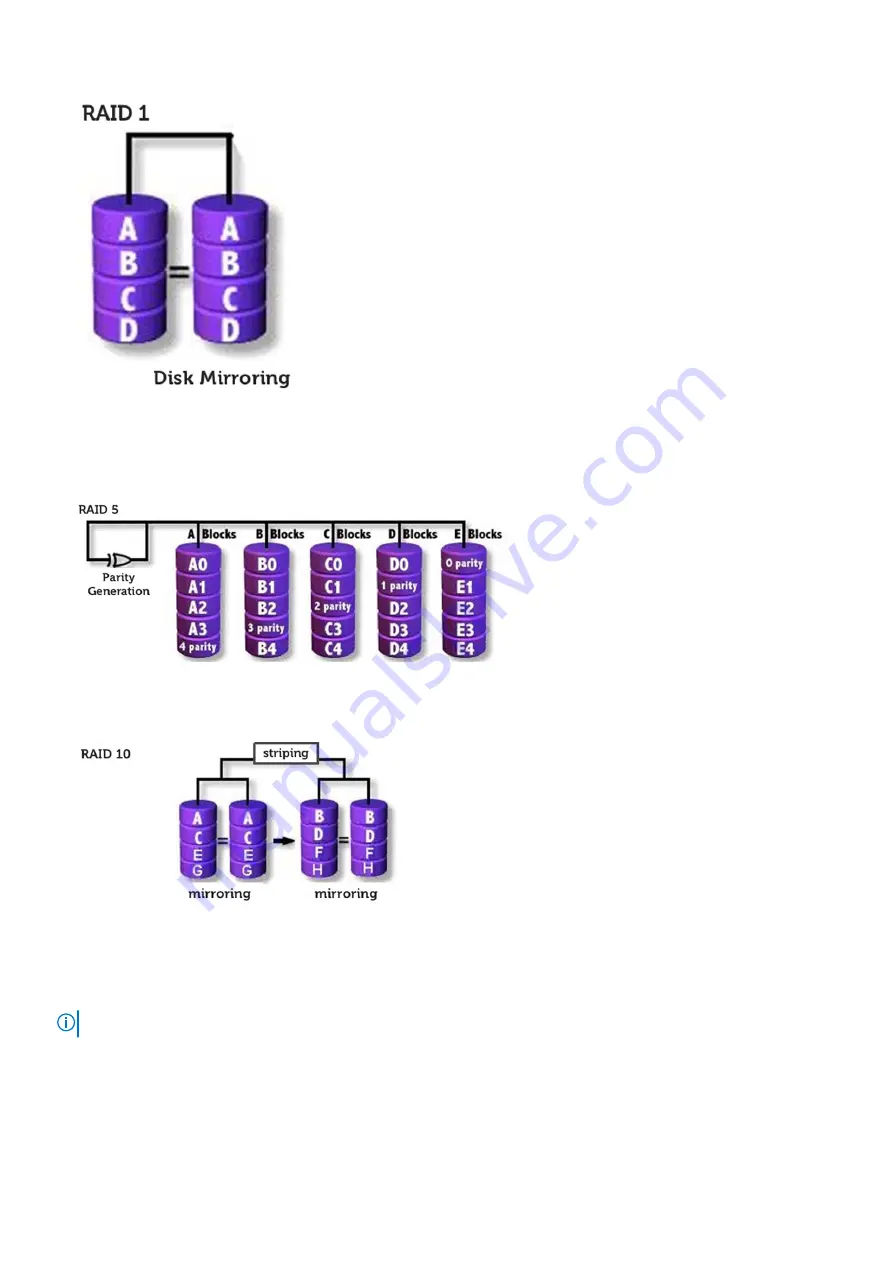
RAID 5 (Striping with Parity):
In this RAID level, data is stripped into blocks and spread across three or more storage devices. Each block contains the
data and a parity for fault tolerance. In an event of a drive failure, the parity helps build the lost piece of data. To further
enhance the write performance, IRST uses Volume Write-Back Cache and Coalescer. The Volume Write-Back allows writes
to be buffered, and Coalescer allows multiple write requests to be combined to reduce the overhead on parity calculation.
4.
RAID 10 (Striping and Mirroring)):
RAID 10 is created, mirroring (RAID 1) the stripped (RAID 0) array. This RAID level uses four or more storage devices. It has
great reliability like a RAID 1 and performance like a RAID 0.
RAID-ready
A RAID-Ready configuration allows migration from one non-RAID SATA drive to a SATA RAID configuration.
NOTE:
A reinstall of the operating system is not required for the migration.
A RAID-Ready computer must meet the following requirements:
●
Supported Intel Chipsets
●
One Serial ATA (SATA) hard drive
●
RAID controller enabled in the computer setup
●
BIOS that includes the IRST option ROM
12
Technology and components
Summary of Contents for D24M
Page 25: ...Steps 1 Rotate the PSU hinge towards the base of the computer Disassembly and reassembly 25 ...
Page 62: ...Figure 5 Heatsink assembly 125 W CPU 62 Disassembly and reassembly ...
Page 71: ...Disassembly and reassembly 71 ...
Page 73: ...Disassembly and reassembly 73 ...
Page 76: ...28 M 2 2230 PCIe x1 slot keyed E for WiFi and Bluetooth card 76 Disassembly and reassembly ...
Page 93: ...Cable cover 93 ...
Page 98: ...Figure 14 Front rubber feet installation 98 Chassis rubber feet ...













































