4 Description of the product
4.1 General description
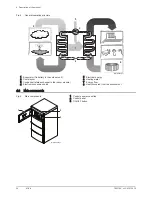
The MIV-4 heat pump comprises:
an indoor module, including a domestic hot water tank and a control
panel.
A reversible outdoor unit for energy production in heating or cooling
mode.
Back-up is possible:
Either via an immersion heater that can be set to 3, 6 or 9 kW (versions
with electrical back-up)
Or via a gas or oil boiler already in use on the installation (versions with
hydraulic back-up).
The indoor module and the outdoor unit are connected by means of refrig
erant and electrical connections.
The indoor module handles heating and domestic hot water production.
The system offers the following advantages:
The heating circuit is housed in the insulated volume within the home.
Thanks to the DC inverter system, the heat pump modulates its output
to adapt to the needs of the home.
The control panel uses the outside sensor to adjust the temperature of
the heating circuit according to the outside temperature.
The steel domestic hot water tank is fitted with a magnesium anode and
lined with food quality standard enamel vitrified at 850°C, which protects
the tank from corrosion.
The heat exchanger in the domestic hot water tank is a coil welded in
side the tank, made of smooth piping. Its external surface, which comes
into contact with drinking water, is enamelled.
The domestic hot water tank is insulated by Chlorofluorocarbon-free pol
yurethane foam, which helps to keep heat losses to a minimum.
4.2 Operating principle
The heat pumps in the MIV-4 range extract the heat found in the air to re
store it to the heating and/or domestic hot water circuit via the refrigerant
fluid. The efficiency of a heat pump is expressed in the form of a coeffi
cient of performance (COP), defined as the ratio between the heat provi
ded and the power consumed.
The heat pump comprises an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser and
an expansion valve. The indoor module includes the condenser. The other
components (evaporator, compressor and expansion valve) are located in
the outdoor unit.
1. The refrigerant fluid in this circuit is converted from the liquid state to
the gaseous state in the evaporator, making it possible to recover heat
from the air.
2. The compressor increases the fluid pressure, which thus increases
the temperature.
3. In the condenser, the fluid transfers the heat to the heating circuit
while converting to the liquid state.
4. The refrigerant passes through the thermostatic expansion valve and
returns to the initial state at low pressure and low temperature before
returning to the evaporator.
4 Description of the product
7623755 - v02 - 03072015
MIV-4
23