DSL-310 ADSL Modem User’s Guide
Chapter 4 - Connecting to the Internet
Now that the setting has been installed, you are ready to establish a connection to the Internet. The
connection from your computer to the Internet is actually an indirect connection. You must first get
connected to the computers that control the connection to the larger network or Internet. Usually, the
ADSL service provider or ISP own the servers that control network access.
Connect with Bridge Mode
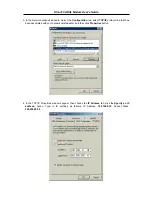
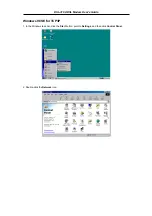
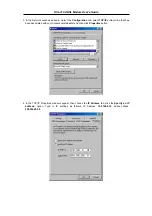
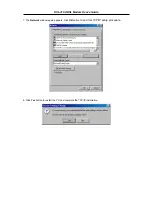
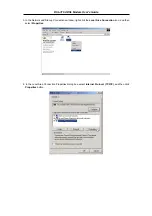
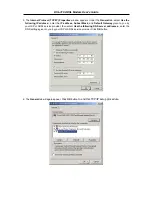
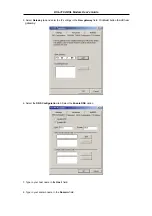
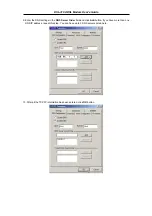
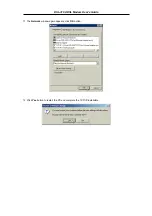
If your ADSL connection uses the RFC1483 protocol, TCP/IP settings must be configured in your system
in order to connect to your service provider’s network (and ultimately connect to the Internet).
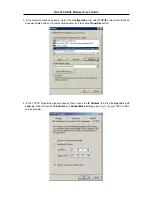
Your ADSL service provider or ISP should give the following information to you:
IP Address . . . . . .
Subnet Mask
Gateway IP Address
DNS Host Name
DNS Domain Name
DNS Server IP Address
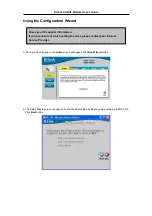
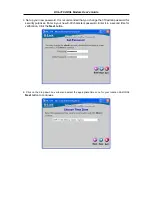
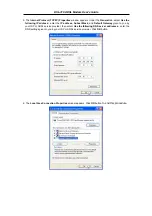
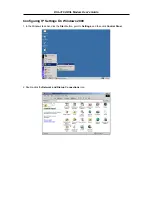
Use the information to configure the Modem. Follow the instructions for your operating system.
IP Address Assignment
IP addresses are 32-bit numbers (in the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 that
uniquely identify every location on the Internet. In order to communicate with sites on the Internet, your
PC must be assigned a unique IP address.
Subnet Mask
This is a bit mask that determines the extent of the subnet that the PC is on. It is used in combination with
an IP address to define areas of the local network that are logically separated from the rest of the network
(subnets). It is in the form
xxx
.
xxx
.
xxx
.
xxx
, where each
xxx
is a number (represented in decimal) between
0 and 255. The value should be 255.0.0.0 for a Class A network, 255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, and
255.255.255.0 for a Class C network, but custom subnet masks are allowed.
It is recommended that you accept the default Subnet Mask suggested by Windows that corresponds to
the class of IP address you entered above.
Gateway Address
This is the IP address of a network device where packets with a destination address outside the current
subnet should be sent. This is usually the address of a router or a host acting as an IP gateway. If your
network is not part of an intranet, or you do not want the Switch to be accessible outside your local
network, you can leave this field unchanged. Sometimes called the
Default Gateway.
DNS Server Address
The Domain Name System (DNS) was designed by the Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG) to
allow locations on the Internet to be identified by a name. A DNS server maintains a database of URLs
(Internet location names) and their corresponding IP addresses. When you type a URL in the
Go To
field
of your web browser, your PC will contact a DNS server to determine the corresponding IP address. To
do this, your PC must know the DNS server’s IP address.
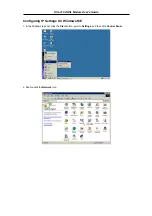
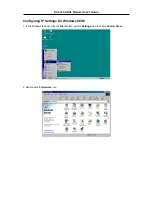
Follow these instructions to configure the IP settings for the operating system installed on your computer.