4
4.
Quickly and repeatedly squeeze the bulb to inflate the cuff on your partner’s arm.
Continue inflating the cuff to a pressure between 150 and 170 mm Hg. The measured
by the sensor value is displayed on the sensor icon in Coach. When the maximum
pressure is reached, set the bulb pump down onto the table. The built-in pressure
release valve will slowly deflate the cuff.
5.
After the pressure drops to 50 mm Hg, press down on the pressure release valve to
release any air left in the cuff. If the pressure does not reach 50 mm Hg by the time data
collection ends, adjust the exhaust rate of the pressure release valve.
Adjusting the Pressure Release Valve
The pressure release valve is set to release at a rate of 3.0 mm Hg/second on an arm of 32
cm in circumference. For arms much larger or much smaller it may be necessary to adjust
the valve so that the exhaust rate stays in the range of 2.0–4.0 mm Hg/s. With the bulb in
hand and the hose leading away from you, place a screwdriver into the metal slot on the
top of the release valve. To increase the rate of exhaust, turn the screwdriver clockwise. To
decrease the rate of exhaust, turn the screwdriver counter-clockwise. The larger a subject’s
arm the slower the release valve will exhaust.
Helpful Tips
Blood pressure readings will
differ from person to person and
even between measurements on
the same individual. Do not
expect to receive the same
measurements each trial since
there are many factors that
cause a person’s blood pressure
to increase or decrease. Use the
following tips to take accurate
measurements.
The subject’s arm and hand
must remain still during
measurements (hand open –
no fist!).
The arm should be at heart
level and is best supported.
Proper placement of the pressure cuff will increase the accuracy of your blood pressure
measurements. The rubber hoses from the cuff should exit over the brachial artery and
2 cm above the crease in the elbow.
Remove any clothing that may cover or constrict the portion of the arm being
measured.
For most individuals it is not necessary to inflate the pressure cuff higher than 170 mm
Hg.
Over inflation of the cuff may cause pain and/or injury
.
If the pressure release valve is exhausting slower or faster than 2.0–4.0 mm Hg /s, then
adjust the exhaust rate of the pressure valve.
There should be at least 10 minutes break between two measurements on the same
individual.
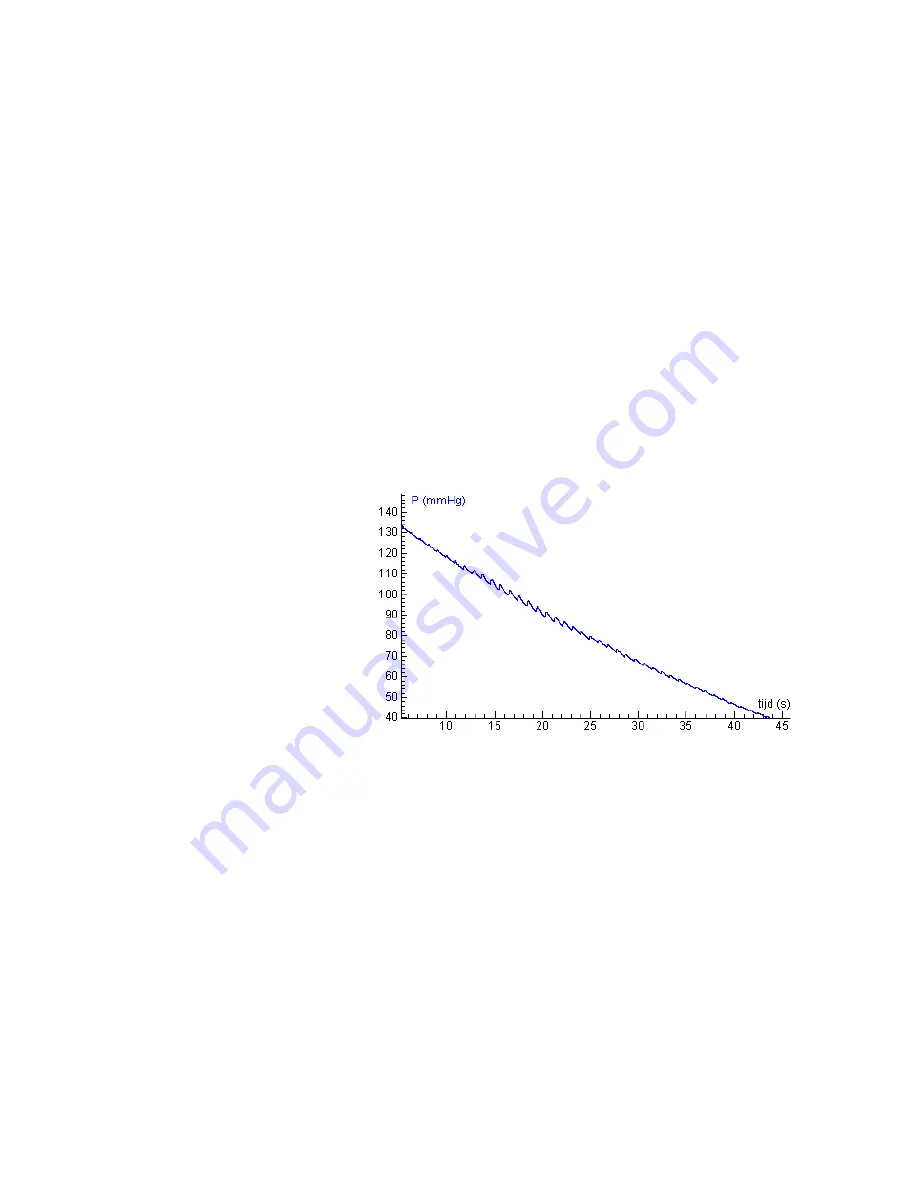
Figure 3.
A typical measurement with the Blood Pressure
sensor. The cuff is slowly deflated and arterial blood
pressure pulses are detected.


























