4-8
Cisco Cable Wideband Solution Design and Implementation Guide, Release 1.0
OL-10705-02
Chapter 4 Implementing and Configuring the Solution
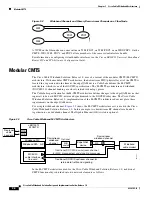
Wideband Cable Modem Behavior
The bonded channel enable option allows the provisioning system to require that a wideband cable
modem operate in traditional DOCSIS 2.0 mode. When the bonded channel enable option has a value of
0 (disable), the CMTS ensures that a wideband-channel interface is not assigned to the wideband cable
modem at registration time.
Only a single occurrence of the bonded channel enable option may be specified in the DOCSIS
configuration file.
Secondary Bonding Group ID
The secondary bonding group ID option is encoded as sub-type 16.
•
Type.Subtype: 43.16
•
Length: 2
•
Value: secondary bonding group ID
The secondary bonding group ID option allows the provisioning system to specify secondary bonded
downstream channels for the wideband cable modem to use. The modem can use one or two secondary
bonded channels for multicast traffic. If the configured secondary bonding group ID is not valid, the
CMTS causes the wideband cable modem to fail registration
Up to two secondary bonding group IDs can be specified in the DOCSIS configuration file. The total of
the RF channels in the primary and secondary bonded channels must comply with the 50 MHz
capture-window limitation of the Linksys WCM300 modem.
Note
If a wideband channel is specified as a secondary bonded channel in the DOCSIS configuration file, the
channel
must be identically specified
as a secondary bonded channel in the CMTS active, running
configuration file. The
cable bonding-group-id
command specifies whether a bonding group is a
primary or secondary bonding group. For information on this command, see the
Cisco uBR10012
Universal Broadband Router SIP and SPA Software Configuration Guide
.
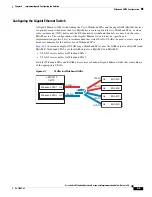
Scientific Atlanta DPC2505 and EPC2505 Modems
The Scientific Atlanta DPC2505 and EPC2505 wideband cable modem makes use of Broadcom
Corporation’s BCM93381 cable modem chip. The BCM93381 chip provides three tuners, allowing the
three downstream receivers to be independently tuned to any frequency. The M-CMTS and the DPC2505
wideband cable modem use these three channels as follows:
•
It uses one of these downstream RF channels as its
primary downstream channel
for MAC
management and signalling messages.
•
It uses the other two downstream RF channels as
non-primary downstream channels
. These two RF
channels can be bonded together to form one wideband channel.
The DPC2505/EPC2505 wideband cable modem uses a selected subset of the DOCSIS 3.0 protocol for
channel bonding. Channel bonding is the transmission of a stream of packets across multiple RF
channels with the use of sequence numbers to ensure the modem receiver delivers packets in the proper
order to the CPE. The DPC2505/EPC2505 wideband cable modem filters packets on a Destination
Address and Security Association Identifier (SAID). The DPC2505/EPC2505 modem supports up to 16
independent re-sequencing contexts.
The DPC2505/EPC2505 wideband cable modem does not support multicast traffic on the wideband
channel. Multicast service flows that the modem sees on the bonded downstream channel are discarded.