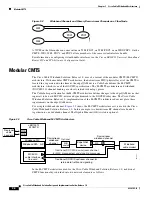
3-8
Cisco Cable Wideband Solution Design and Implementation Guide, Release 1.0
OL-10705-02
Chapter 3 Cisco Cable Wideband Architecture
Gigabit Ethernet Switch Functionality
Quality of Service
For quality of service (QoS) on a wideband downstream channel, a wideband cable modem can be
assigned multiple service flows. Only Best Effort (BE) service flows are currently supported. The CMTS
sends data traffic on a non-guaranteed best-effort basis.
For the traditional DOCSIS upstream channel associated with a wideband channel, QoS capabilities
supported are identical to those in DOCSIS 2.0.
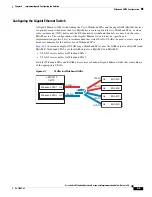
Gigabit Ethernet Switch Functionality
The Gigabit Ethernet (GE) switch is an optional device that receives downstream packets from the Cisco
Wideband SPA and passes the packets to the edge QAM device. The Gigabit Ethernet switch is used for
these purposes:
•
To concentrate traffic from multiple Gigabit Ethernet links to a smaller number of Gigabit Ethernet
links prior to fiber transport to the edge QAM devices
•
To provide 1+1 or N+1 redundancy for downstream Gigabit Ethernet links
•
To multiplex wideband DOCSIS traffic and video traffic onto the same edge QAM devices
If more than two EQAM devices are required for two Wideband SPAs, a Gigabit Ethernet switch is
needed to connect the SPAs to the EQAM devices.
If video-on-demand (VOD) traffic and the RF channels for wideband channels are mixed on the same
EQAM device, a Gigabit Ethernet switch is required.
When an RF channel for a wideband channel is configured using Cisco IOS commands on the uBR10012
router, the
rf-channel
command’s
mac-address
argument specifies the MAC address for the next-hop
interface on the switch if it is a Layer-2 GE switch. The
rf-channel
command’s
ip-address
argument
specifies the IP address of the Gigabit Ethernet interface on the edge QAM device. The MAC address on
the switch and the IP address on the EQAM device are used to route downstream traffic for the RF
channel to the correct destinations.
Edge QAM Device Functionality
The edge QAM (EQAM) device receives wideband as MPEG-TS over IP on its Gigabit Ethernet
interfaces. The edge QAM device extracts the MPEG-TS packets from the MPEG-TS over IP stream and
routes them to the proper QAM RF outputs to the HFC plant for transmission to the wideband cable
modem.
The edge QAM devices are not involved in the active management of bandwidth or QOS for wideband
channels. The edge QAM devices are not aware of the IP addressing used by the wideband cable
modems.
A single QAM’s total bandwidth can be divided up and statically allocated to more than one wideband
channel. When a wideband channel is configured on the CMTS, the wideband channel uses multiple
specified logical RF channels on the Wideband SPA. Each RF channel is associated with a QAM output
on the edge QAM device.The bandwidth of an RF channel can be divided between one or more wideband
channels as long as the total allocated bandwidth for an RF channel (and QAM) does not exceed 100
percent. For more information on configuring RF channels, see the
Cisco uBR10012 Universal
Broadband Router SIP and SPA Software Configuration Guide
.