n
If an endpoint is registered to the VCS, the VCS will be able to forward inbound calls to that endpoint.
n
If the VCS is not configured with any SIP domains, the VCS will act as a SIP server. It may proxy
registration requests to another registrar, depending upon the
SIP registration proxy mode
setting.
Registration refresh intervals
Depending on the typical level of active registrations on your system, you may want to configure the
Standard registration refresh strategy
to
Variable
and set the refresh intervals as follows:
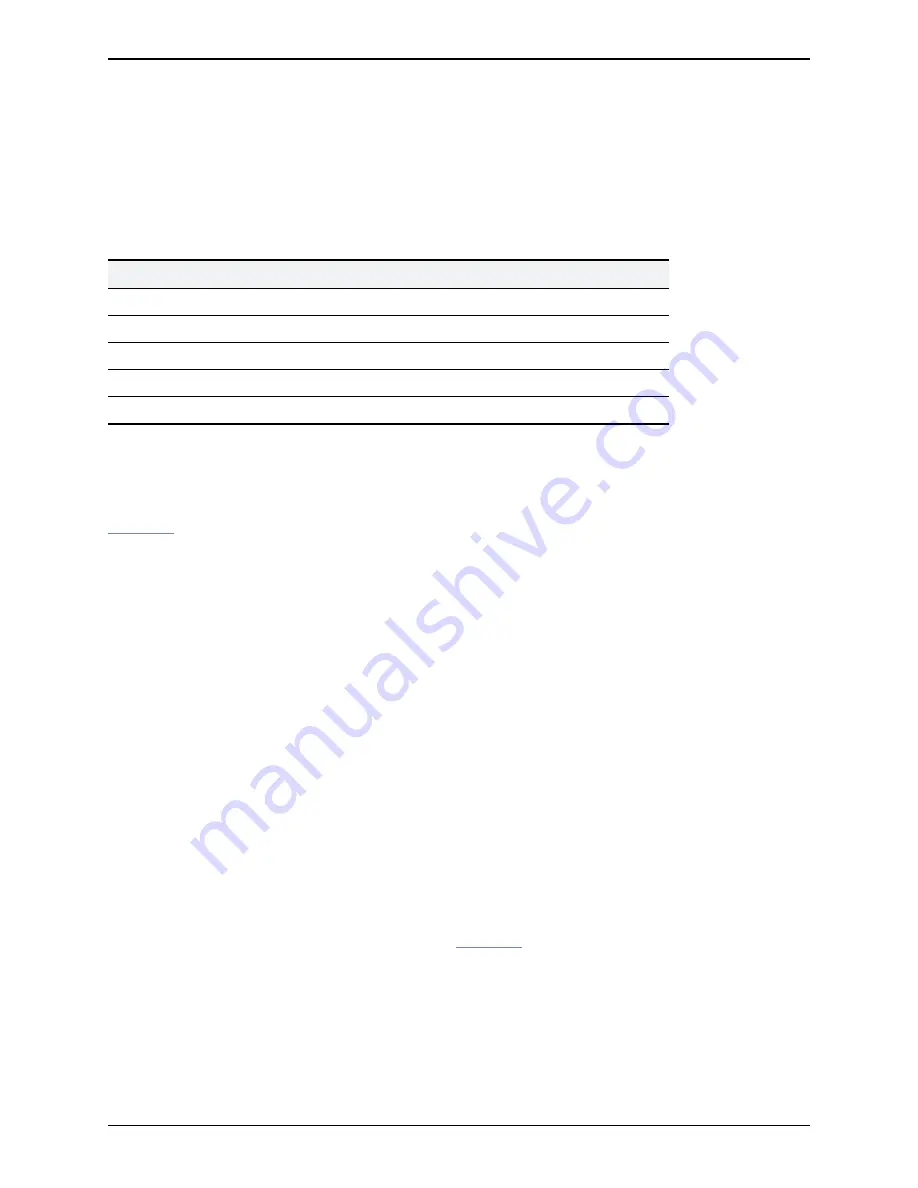
Active registrations
Minimum refresh interval
Maximum refresh interval
1–100
45
60
101–500
150
200
501–1000
300
400
1000–1500
450
800
1500+
750
1000
If you want to ensure registration resiliency, use SIP outbound registrations as described below.
SIP registration resiliency
The VCS supports multiple client-initiated connections (also referred to as "SIP Outbound") as outlined in
RFC 5626
.
This allows SIP endpoints that support
RFC 5626
to be simultaneously registered to multiple VCS cluster
peers. This provides extra resiliency: if the endpoint loses its connection to one cluster peer it will still be able
to receive calls via one of its other registration connections.
VCS as a SIP proxy server
The VCS acts as a SIP proxy server when
SIP mode
is enabled. The role of a proxy server is to forward
requests (such as REGISTER and INVITE) from endpoints or other proxy servers on to further proxy servers
or to the destination endpoint.
The VCS's behavior as a SIP proxy server is determined by:
n
the SIP registration proxy mode setting
n
the presence of Route Set information in the request header
n
whether the proxy server from which the request was received is a neighbor of the VCS
A Route Set specifies the path to take when requests are proxied between an endpoint and its registrar. For
example, when a REGISTER request is proxied by the VCS, it adds a path header component to the request.
This signals that calls to that endpoint should be routed through the VCS. This is usually required in
situations where firewalls exist and the signaling must follow a specified path to successfully traverse the
firewall. For more information about path headers, see
RFC 3327
.
When the VCS proxies a request that contains Route Set information, it forwards it directly to the URI
specified in the path. Any call processing rules configured on the VCS are bypassed. This may present a
security risk if the information in the Route Set cannot be trusted. For this reason, you can configure how the
VCS proxies requests that contain Route Sets by setting the
SIP registration proxy mode
as follows:
Cisco VCS Administrator Guide (X8.1.1)
Page 82 of 507
Protocols
About SIP






























