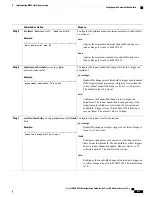
DETAILED STEPS
Purpose
Command or Action
Enters global configuration mode.
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 1
Enters the explicit path configuration mode. Identifer range is
1 to 65535.
explicit-path {identifier number [disable | index]}{
name explicit-path-name
}
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# explicit-path
name backup-srlg
Step 2
Specifies the IP address to be excluded from the explicit path.
index 1 exclude-address
192.168.92.1
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router
router(config-expl-path)# index 1
exclude-address 192.168.92.1
Step 3
Specifies the IP address to extract SRLGs to be excluded from
the explicit path.
index 2 exclude-srlg 192.168.92.2
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-expl-path)# index
2 exclude-srlg 192.168.192.2
Step 4
commit
—
Saves the configuration changes and remains within
the configuration session.
Use the
commit
or
end
command.
Step 5
end
—
Prompts user to take one of these actions:
•
Yes
—
Saves configuration changes and exits the
configuration session.
•
No
—
Exits the configuration session without committing
the configuration changes.
•
Cancel
—
Remains in the configuration session, without
committing the configuration changes.
Related Topics
MPLS Traffic Engineering Shared Risk Link Groups, on page 198
Explicit Path, on page 199
Fast ReRoute with SRLG Constraints, on page 199
Importance of Protection, on page 201
Delivery of Packets During a Failure, on page 202
Multiple Backup Tunnels Protecting the Same Interface , on page 202
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide for the Cisco CRS Router, Release 5.1.x
297
Implementing MPLS Traffic Engineering
Configuring the Shared Risk Link Groups