12-15
Cisco ASA Series Firewall CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 12 Getting Started with Application Layer Protocol Inspection
Configure Regular Expressions
Configure Regular Expressions
Regular expressions define pattern matching for text strings. You can use these expressions in some
protocol inspection maps to match packets based on strings such as URLs or the contents of particular
header fields.
•
Create a Regular Expression, page 12-15
•
Create a Regular Expression Class Map, page 12-17
Create a Regular Expression
A regular expression matches text strings either literally as an exact string, or by using
metacharacters
so that you can match multiple variants of a text string. You can use a regular expression to match the
content of certain application traffic; for example, you can match a URL string inside an HTTP packet.
Before You Begin
Use
Ctrl+V
to escape all of the special characters in the CLI, such as question mark (?) or a tab. For
example, type
d[Ctrl+V]?g
to enter
d?g
in the configuration.
See the
regex
command in the command reference for performance impact information when matching
a regular expression to packets. In general, matching against long input strings, or trying to match a large
number of regular expressions, will reduce system performance.
Note
As an optimization, the ASA searches on the deobfuscated URL. Deobfuscation compresses multiple
forward slashes (/) into a single slash. For strings that commonly use double slashes, like “http://”, be
sure to search for “http:/” instead.
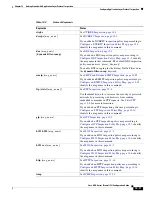
The following table lists the metacharacters that have special meanings.
Table 12-3
Regular Expression Metacharacters
Character Description
Notes
.
Dot
Matches any single character. For example,
d.g
matches
dog, dag, dtg, and any word that contains those
characters, such as doggonnit.
(
exp
)
Subexpression
A subexpression segregates characters from surrounding
characters, so that you can use other metacharacters on
the subexpression. For example,
d(o|a)g
matches dog
and dag, but
do|ag
matches do and ag. A subexpression
can also be used with repeat quantifiers to differentiate
the characters meant for repetition. For example,
ab(xy){3}z
matches abxyxyxyz.
|
Alternation
Matches either expression it separates. For example,
dog|cat
matches dog or cat.
?
Question mark
A quantifier that indicates that there are 0 or 1 of the
previous expression. For example,
lo?se
matches lse or
lose.
Summary of Contents for ASA 5508-X
Page 11: ...P A R T 1 Access Control ...
Page 12: ......
Page 157: ...P A R T 2 Network Address Translation ...
Page 158: ......
Page 233: ...P A R T 3 Service Policies and Application Inspection ...
Page 234: ......
Page 379: ...P A R T 4 Connection Management and Threat Detection ...
Page 380: ......