9-19
Cisco ASA Series Firewall CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 9 Network Address Translation (NAT)
Dynamic PAT
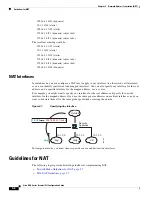
The following figure shows a typical dynamic PAT scenario. Only real hosts can create a NAT session,
and responding traffic is allowed back. The mapped address is the same for each translation, but the port
is dynamically assigned.
Figure 9-4
Dynamic PAT
After the connection expires, the port translation also expires. For multi-session PAT, the PAT timeout is
used, 30 seconds by default. For per-session PAT, the xlate is immediately removed. Users on the
destination network cannot reliably initiate a connection to a host that uses PAT (even if the connection
is allowed by an access rule).
Note
For the duration of the translation, a remote host can initiate a connection to the translated host if an
access rule allows it. Because the port address (both real and mapped) is unpredictable, a connection to
the host is unlikely. Nevertheless, in this case you can rely on the security of the access rule.
Dynamic PAT Disadvantages and Advantages
Dynamic PAT lets you use a single mapped address, thus conserving routable addresses. You can even
use the ASA interface IP address as the PAT address.
Dynamic PAT does not work with some multimedia applications that have a data stream that is different
from the control path. See
Default Inspections and NAT Limitations, page 12-6
for more information
about NAT and PAT support.
Dynamic PAT might also create a large number of connections appearing to come from a single IP
address, and servers might interpret the traffic as a DoS attack. You can configure a PAT pool of
addresses and use a round-robin assignment of PAT addresses to mitigate this situation.
PAT Pool Object Guidelines
When creating network objects for a PAT pool, follow these guidelines.
For a PAT pool
•
If available, the real source port number is used for the mapped port. However, if the real port is
not
available, by default the mapped ports are chosen from the same range of ports as the real port
number: 0 to 511, 512 to 1023, and 1024 to 65535. Therefore, ports below 1024 have only a small
PAT pool that can be used. (8.4(3) and later, not including 8.5(1) or 8.6(1)) If you have a lot of traffic
that uses the lower port ranges, you can specify a flat range of ports to be used instead of the three
unequal-sized tiers: either 1024 to 65535, or 1 to 65535.
•
If you use the same PAT pool object in two separate rules, then be sure to specify the same options
for each rule. For example, if one rule specifies extended PAT and a flat range, then the other rule
must also specify extended PAT and a flat range.
10.1.1.1:1025
209.165.201.1:2020
In
s
ide
O
u
t
s
ide
10.1.1.1:1026
209.165.201.1:2021
10.1.1.2:1025
209.165.201.1:2022
130034
S
ec
u
rity
Appli
a
nce
Summary of Contents for ASA 5508-X
Page 11: ...P A R T 1 Access Control ...
Page 12: ......
Page 157: ...P A R T 2 Network Address Translation ...
Page 158: ......
Page 233: ...P A R T 3 Service Policies and Application Inspection ...
Page 234: ......
Page 379: ...P A R T 4 Connection Management and Threat Detection ...
Page 380: ......