Section 3: Operation
Mirage S+/HD, Matrix S+/HD, Christie HD/DS/DW, DLV User’s Manual
3-25
020-100001-04 Rev. 1 (12/07)
- Software v1.6g or higher
.
setting. In high ambient light conditions, lower gamma may produce better results
than higher gamma. Gamma of 2.2 (default) indicates the gamma table has not been
adjusted. For more information, refer to
Advanced Image Settings
submenu,
Gamma
Table
. Again, good gamma improves contrast while maintaining good details for
blacks.
Filter
The proper filter setting is automatically set for virtually all
signals, and rarely needs to be changed. It applies a low pass
filter for noise reduction in the incoming input signal,
particularly for HDTV or SDTV. Applied in the analog domain
before sampling, this filtering removes high frequencies and
thus reduces pixel phase noise (note this also reduces signal
bandwidth). Override only if standard pixel tracking and phase
adjustments do not adequately clear up a “noisy” video signal, or if a graphics signal
appears overly “soft”. Both instances indicate that “Filter” may be set to the wrong
option.
Detail
“Detail” adjusts the sharpness of a video image so that edges remain clearly defined. It
can be particularly useful if a significant “Noise Reduction” adjustment has caused the
image to appear too soft. Adjust until the display is as sharp as desired, keeping in
mind that because “Detail” adds some high frequencies back into the image, it can
also re-introduce a certain degree of noise.
Noise Reduction
“Noise Reduction” is similar to the “Filter” control, but operates in the post-sampling
digital domain with a more subtle effect. Higher settings are most useful for clearing
up noisy RGB images such as those from a PC. Adjust as desired, keeping in mind
that reducing noise (which reduces high frequencies) may also soften the image.
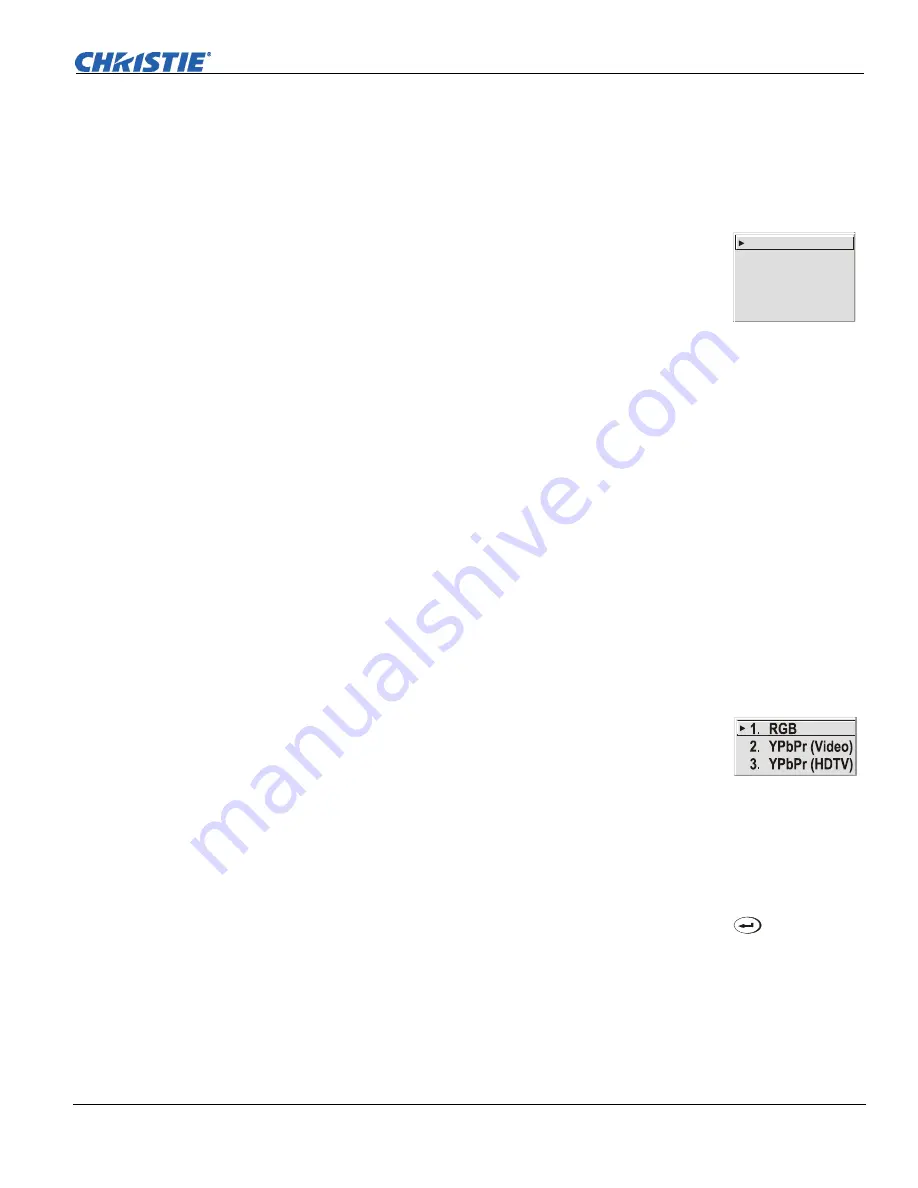
Color Space
“Color Space” determines how the color components of an
analog input signal are decoded for accurate color in the display.
Selecting a color space option is useful only for analog signals
and certain digital sources connected to
INPUT 1, INPUT 2, INPUT
5
or
INPUT 6.
Although color space for these analog signals is
automatically determined by the projector, in some circumstances you may wish to
override this and manually set a specific color space.
NOTE:
For many digital signals or for signals connected to
INPUT 3
or
INPUT 4
, the
color space function is entirely automatic and the pull-down list disabled.
The current color space appears in the
Image Settings
menu. Press
to select a
different option:
•
Select
RGB
unless
you are using component video at
INPUT 1, 2, 5
or
6.
•
Select
YPbPr (Video)
with a standard definition televised signal (SDTV).
•
Select
YPbPr
(HDTV)
with a high definition televised signal (HDTV).
Off
RGB
HDTV
EDTV
SDTV
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.






























