Module RF450
U077.0.2-MRF450
8
7.0 Communication
Protocol
Communication between the module and host is packetized. Each packet begins with a start-of-
packet (SOP) indicator, followed by the length of the packet message, followed by the message,
and terminated with a checksum calculated over the message. All multi-byte fields are
interpreted in little-endian format; the LSB is stored in the lowest address and the MSB is stored
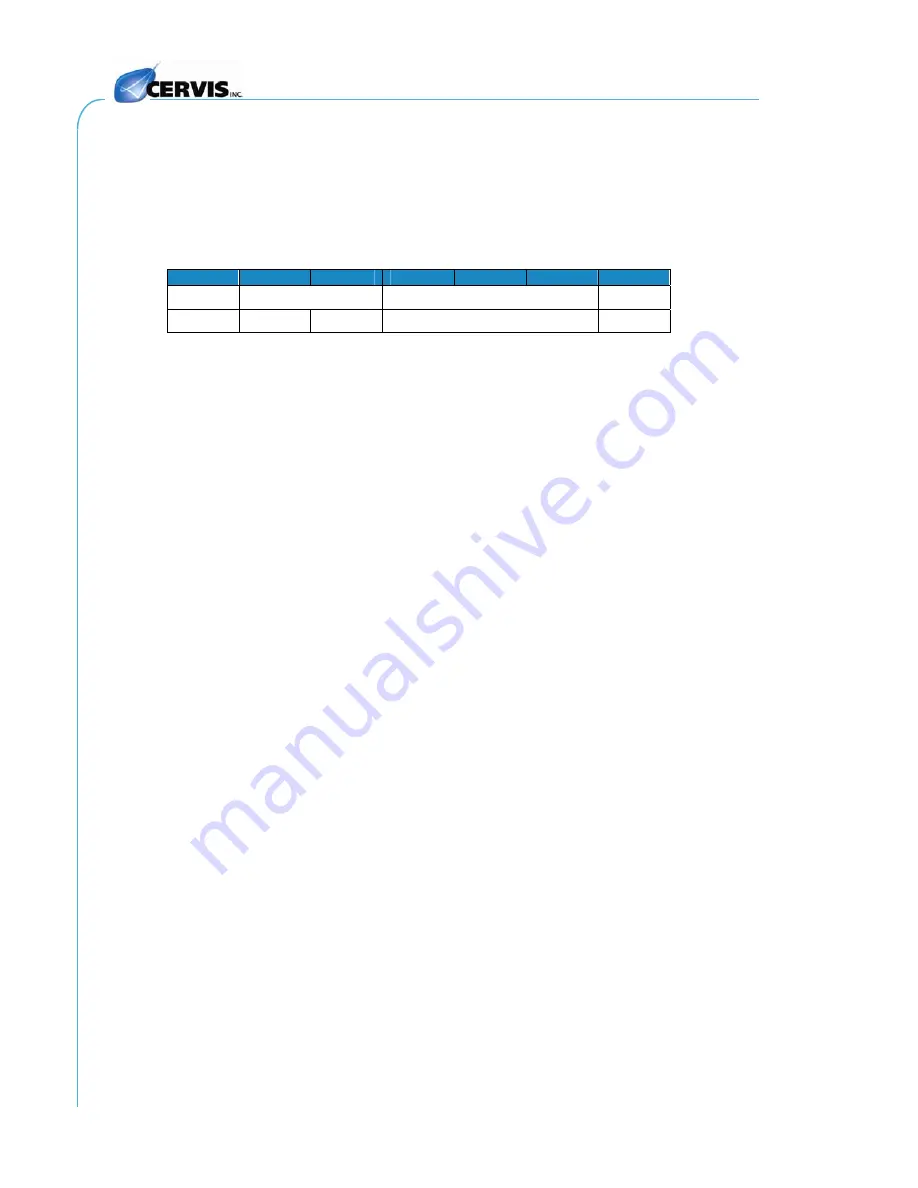
in the highest. A diagram of the packet format follows.
Table 4. Packet Format Diagram
0
1
2
3
..
n
n + 1
SOP
Message Length
Message
Chksum
0x3C LSB MSB
Chksum
Region
The checksum is calculated by subtracting the 8-bit sum of the message bytes from 0xFF. In
this way, the checksum of a packet can be easily verified by summing the message bytes and
checksum. The result of a valid packet is 0xFF.
Handshaking
The synchronization scheme between the module and host varies depending on the
communication channel selected. In either scheme the packet structure remains constant.
7.1 SPI
In SPI mode the module is a slave device. As such, it cannot initiate communications. All
communication is controlled by the host. The module utilizes a buffer for all packets to the host.
F0 (P1.9) is used to communicate the buffer status to the host. When F0 is low, there are no
packets available for the host. When F0 is high, at least one packet is available.
The host must check the state of F0 prior to initiating a SPI transfer. If F0 is low the transaction
will be handled as a write. No data will be shifted out to the host during the transaction. If F0 is
high the transaction will be handled as a read. The module will shift the buffered packet to the
host. Data shifted from the host to the module will be ignored. The polarity of this signal may be
configured (see Pin Mode parameter).
In order to prevent SPI slave overflows, a second control signal is implemented. F1 is utilized as
a CTS (clear to send) signal. The host must check the state of F1 prior to initiating a SPI
transfer. If F1 is asserted the SPI slave interface is busy completing a previously requested
command and any new request will be silently discarded. As soon as nSS is asserted, F1 is
asserted. F1 remains asserted until the requested command completes. The polarity of this
signal may be configured (see Pin Mode parameter).
Due to the structured nature of SPI the likelihood that the module and host lose sync is low. No
additional facilities are provided in this mode.
7.2 UART
In UART mode, both the host and module can initiate communications. In this mode no special
handshaking is required.
In this mode it is potentially possible that the module and host lose sync due to the fact that the
SOP byte can occur as valid data. In order to recover from this condition the protocol also
provides some simple event timeouts. There is no timeout associated with waiting for the SOP
indicator. Once the SOP has been detected an inter-byte timer is started. If the inter-byte
timeout expires an error message is sent to the host and the current packet is discarded. A last-
byte timer is also maintained. This last-byte timer must elapse before an error message is sent.
This ensures that an error message is not sent until the host has completed.