97
Statistical Graphs and Calculations
Chapter 7
k
k
k
k
k
Inputting Data into Lists
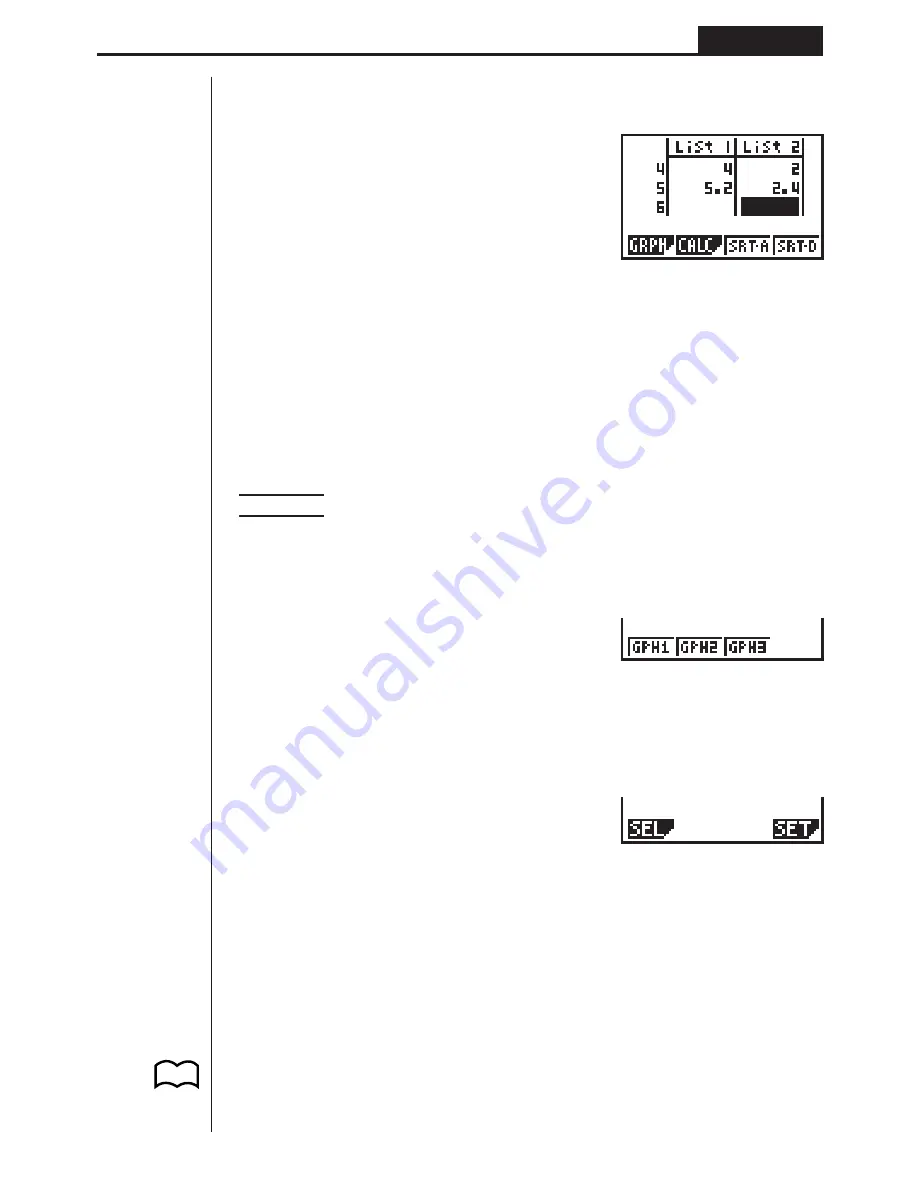
Input the two groups of data into List 1 and List 2.
a.f
w
b.c
w
c.e
w
e
w
f.c
w
e
-
c.b
w
a.d
w
b.f
w
c
w
c.e
w
Once data is input, you can use it for graphing and statistical calculations.
• Input values can be up to 10 digits long (9-digit mantissa and 2-digit exponent
when using exponential format). Values in statistical data table cells are shown
only up to six digits.
• You can use the
f
,
c
,
d
and
e
keys to move the highlighting to any cell in
the lists for data input.
k
k
k
k
k
Plotting Data
Example
To specify Graph 1 as non-draw (OFF) and Graph 3 as draw (ON)
and use Graph 3 to plot the data you input into statistical data
List 1 and List 2 above
While the statistical data list is on the display, press
1
(GRPH) to display the graph
menu.
1
(GRPH)
1
(GPH1) ..... Graph 1 draw
2
(GPH2) ..... Graph 2 draw
3
(GPH3) ..... Graph 3 draw
[
1
(SEL) ......... Graph (GPH1, GPH2, GPH3) selection
4
(SET) ......... Graph settings (graph type, list assignments)
Press
[
to return to the previous menu.
• You can specify the graph draw/non-draw status, the graph type, and other gen-
eral settings for each of the graphs in the graph menu (GPH1, GPH2, GPH3).
• You can press any function key (
1
,
2
,
3
) to draw a graph regardless of the
current location of the highlighting in the statistical data list.
• The initial default graph type setting for all the graphs (Graph 1 through Graph 3)
is scatter diagram, but you can change to one of a number of other graph types.
P.99
1
2
3
4
[
1
2
3
4
[
Summary of Contents for fx-7400G PLUS
Page 7: ... fx 7400G PLUS ...
Page 14: ...xii Contents ...
Page 57: ...Differential Calculations Chapter 3 ...
Page 176: ...162 Chapter 8 Programming ...
Page 188: ...Chapter 9 Data Communications 174 ...
Page 199: ...185 1 2 3 4 5 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display ...
Page 200: ...186 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display 6 7 8 9 10 ...
Page 201: ...187 11 12 13 14 15 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display ...
Page 202: ...188 16 17 18 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display ...
Page 205: ...191 1 2 3 4 5 Program for Rotating a Figure No 5 Step Key Operation Display ...
















































