III-12
5.
HIGH-VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY ASSY
5.1 Outline
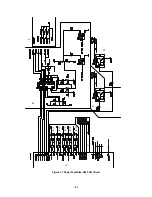
The High-Voltage Power Supply Assy supplies the high-voltage for the charging roller,
the developer cylinder and the transfer roller according to the engine CPU’s control
signals.
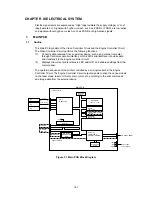
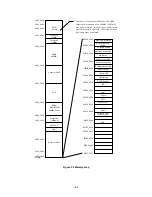
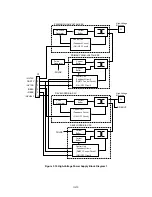
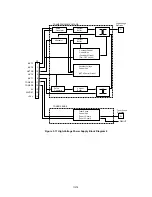
The block diagrams are shown Fig 3.10 and 3.11.
5.2
Operation of the Components of the High-Voltage Power Supply Assy
(1) Primary
charging
When input signal/HV1AC gets the Low level, the primary high-voltage AC is
applied to the primary charging roller. And when input signal/HV1DC gets the Low
level, the primary high-voltage DC is applied to the primary charging roller. The
primary high-voltage DC changes with developer bias DC according to values of
the input signal DNSTY which is for print density adjustment.
(2) Developer
bias
When input signal/DBAC gets the Low level, the developer bias AC is applied to
the developer cylinder. And when input signal/DBDC gets the Low level, the
developer bias DC is applied to the developer cylinder. The developer bias DC
changes according to values of the input signal DNSTY which is for print density
adjustment, like the primary high-voltage DC.
(3) Transfer
charging
Transfer bias is controlled by the input signals HVT1 - 4 and HVTFB. When the
input signal/HVT1 gets the Low level and the input signal HVT4 gets 3.7V, negative
high-voltage is applied to the transfer roller. When the input signal/HVT2 gets the
Low level, positive high-voltage is applied to the transfer roller. When the input
signal/HVT3 gets the Low level, positive high-voltage about 1100 times that of the
input signal HVT4 is applied to the transfer roller. The input signal HVTFB has
voltage about 1/1100 times the positive voltage generated on the transfer roller.
Once the engine CPU is informed of this voltage, the bias applied to the transfer
roller can be known.
Note: The HVT2 signal generates high-voltage irrespective of the HVT4 signal.
(4) Toner
sensing
Voltage levels of the input signals TONER1 and TONER2 allow the engine CPU to
check if the cartridge is set or not and if toner is empty. The TONER1 carries the
voltage generated at the toner sensor and the TONER2 carries the developing bias
output value.
Summary of Contents for HL-2060
Page 1: ...MECHANICS ELECTRONICS SERVICE MANUAL LASER PRINTER ...
Page 41: ...III 8 A B F C D E 1 E 2 E 3 E 4 E 5 F Figure 3 7 Paper Feed Size SW PCB Circuit ...
Page 129: ...VII 16 Test for memory MEMORY DISPLAY MEMORY DEBUG MEMORY TEST exit MENU ...
Page 137: ...Appendix A 3 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 1 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 1 7 NAME A 3 ...
Page 138: ...Appendix A 4 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 2 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 2 7 NAME A 4 ...
Page 139: ...Appendix A 5 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 3 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 3 7 NAME A 5 ...
Page 140: ...Appendix A 6 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 4 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 4 7 NAME A 6 ...
Page 141: ...Appendix A 7 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 5 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 5 7 NAME A 7 ...
Page 142: ...Appendix A 8 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 6 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 6 7 NAME A 8 ...
Page 143: ...Appendix A 9 Main PCB Circuitry Diagram 7 7 CODE UK4058000 B512006 CIR 7 7 NAME A 9 ...
Page 144: ...Appendix A 10 Control Panel PCB Circuitry Diagram 1 1 CODE UK4077000 B512005 CIR NAME A 10 ...
Page 145: ...Appendix A 11 Laser LD PCB Circuitry Diagram 1 1 CODE UK3253000 B48K253 CIR NAME A 11 ...
Page 147: ...June 98 54T046NE0 HL2060 ...