30
en | General installation procedures and instructions
PRAESENSA
2019.11 | V1.00 |
Installation manual
Bosch Security Systems B.V.
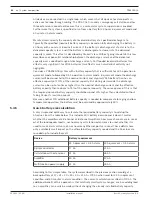
For static Dante audio input streams, the PRAESENSA system controller does support
glitch‑free audio redundancy. This is possible because these Dante sources are not controlled
by the system controller. To use this feature, the primary network must be connected to one
of the ports 1 to 4 of the system controller, the secondary network must be connected to
port
5. The Dante connections must be set up using Dante Controller software.
Notice!
1000BASE‑T Ethernet connections use all four wire pairs in a standard CAT5e cable (or
better), while 100BASE‑TX uses only two pairs. Most Ethernet switches have a feature that a
1000BASE‑T port falls back to 100BASE‑TX when a connected cable has a fault of some sort
in any of its eight wires. In a system that is using RSTP for cable redundancy, it is important
that this fallback feature is disabled, because a 100
Mbps connection is still considered a
valid connection and RSTP will not replace it by an alternative high speed 1
Gbps-link. All
PRAESENSA devices have this fallback mechanism disabled to allow RSTP to work properly.
4.6.10
IP-addressing
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique address which identifies hardware over the
network such as a computer, server, system controller, switch, call station or amplifier. It
allows a device to communicate with other devices over an IP‑based network such as the LAN
or WAN. There are multiple possibilities for assigning an IP‑address to a device: Link‑Local,
DHCP and manual (static) assignment:
–
Link‑Local
addresses are automatically assigned by the individual devices in cases where
no static IP‑addressing is assigned and a DHCP‑server is not found (IPv4LL). Addressing
is based on the MAC-address of the device. Link‑Local addressing can be recognized by
an IP‑address within the range of 169.254.0.0/16 (169.254.0.1 - 169.254.255.254) with
subnet‑mask 255.255.0.0. Do not use 255.255.255.0 as subnet‑mask! This Link‑Local
addressing is also known as Automatic Private IP‑Addressing (APIPA-addressing). The
Link‑Local addressing scheme manages fixed IP‑addresses in the same range, as the
devices automatically check availability of the IP‑address to ensure devices that do not
support IPv4LL can operate in the same subnet. IPv4LL addressing only supports a single
subnet; this IP‑address range is not routable, so will be dropped by a router.
–
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) is a technology used to assign
IP‑addresses and other related configuration information (such as subnet mask and
default gateway) automatically to each device on a network. This is achieved by using a
device that contains a DCHP‑server, a feature frequently found in devices such as routers
or an ARNI. As long as all devices are within the same subnet, IPv4LL is the preferred way
of address assignment. When using DHCP, make sure the DHCP‑server is powerful
enough, because all devices will request an address immediately after the system
switches on.
–
Manually assigned IP-addresses
, also known as static or fixed IP‑addressing, are only
recommended if there is a good understanding of the network administration and
assigned IP‑addressing schemes already in place on the network. This is critical for
preventing collisions and invalid or duplicate IP‑addresses on the network. It is
mandatory to enter a valid IP‑address and subnet mask, while it is optional to enter a
default gateway and DNS‑server address. The default gateway is mandatory when data
goes outside the local area network (LAN) and the DNS‑server is mandatory when an
ARNI is used within the system. If there is a DHCP‑server active, in addition to using fixed
IP‑addresses, it is recommended to exclude the fixed IP‑addresses from the
DHCP‑address range. Currently PRAESENSA does not support manually assigned
IP‑addresses.
Summary of Contents for PRAESENSA
Page 1: ...PRAESENSA Public Address and Voice Alarm System en Installation manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 193: ......