3-1-7. Virtual Stack
Function name:
Virtual Stack
Function description:
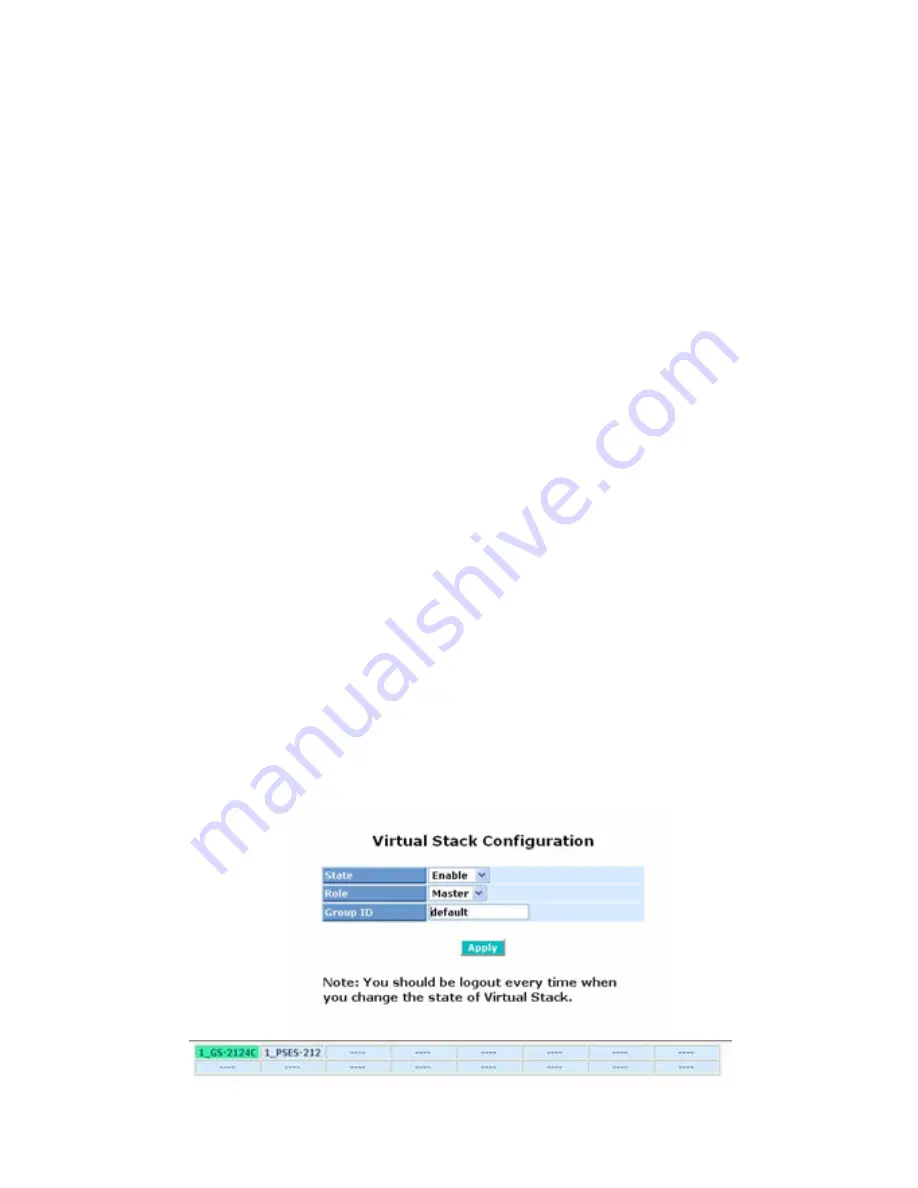
Virtual Stack Management(VSM) is the group management function. Through
the proper configuration of this function, switches in the same LAN will be
grouped automatically. And among these switch, one switch will be a master
machine, and the others in this group will become the slave devices.
VSM offers a simple centralized management function. It is not necessary to
remember the address of all devices, manager is capable of managing the
network with knowing the address of the Master machine. Instead of SNMP or
Telnet UI, VSM is only available in Web UI. While one switch become the
Master, two rows of buttons for group device will appear on the top of its Web
UI. By pressing these buttons, user will be allowed to connect the Web UI of
the devices of the group in the same window without the login of these device.
The most top-left button is only for Master device(See Fig.3-9). The
background color of the button you press will be changed to represent that the
device is under your management.
Note: It will remove the grouping temporarily in case that you login the switch
via the console.
The device of the group will be shown as station address ( the last number of
IP Address) + device name
on the button (e.g. 196_GS-2224L), otherwise it
will show ” ---- “ if no corresponding device exists.
Once the devices join the group successfully, then they are merely able to be
managed via Master device, and user will fail to manage them via
telnet/console/web individually.
Up to 16 devices can be grouped for VSM, however, only one Master is
allowed to exist in each group. For Master redundancy, user may configure
more than two devices as Master device, however, the Master device with the
smaller MAC value will be the Master one. All of these 16 devices can
become Master device and back up with each other .
Fig. 3-10-1
Summary of Contents for L2 Plus
Page 1: ......
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...16 Port SFP 8 Port Combo GbE L2 Plus Managed Switch...
Page 4: ...2...
Page 36: ...34 Fig 2 15 Office Network Connection Fig 2 14 Peer to peer Network Connection...
Page 56: ......
Page 78: ...22 Fig 3 24...
Page 81: ...25 Fig 3 26...
Page 88: ...32 Fig 3 31...
Page 96: ...40 Fig 3 39 Fig 3 40 Fig 3 41...
Page 112: ...56 Fig 3 62 Set up VLAN Tag Priority Mapping Finish...
Page 119: ...63 Fig 3 67 Ingress Port Fig 3 68...
Page 121: ...65 Fig 3 70...
Page 122: ...66 Fig 3 71 Fig 3 72 Fig 3 73 ARP...
Page 123: ...67 Fig 3 74 ARP Fig 3 75 ARP Fig 3 76 ARP Fig 3 77 ARP...
Page 124: ...68 Fig 3 78 ARP Fig 3 79 ARP Fig 3 80 ARP Fig 3 81 ARP...
Page 125: ...69 Fig 3 82 ARP Fig 3 83 ARP Fig 3 84 ARP Fig 3 85 ARP Fig 3 86 ARP...
Page 126: ...70 Fig 3 87 IPv4 Fig 3 88 IPv4 Fig 3 89 IPv4...
Page 127: ...71 Fig 3 90 IPv4 Fig 3 91 IPv4 Fig 3 92 IPv4 Fig 3 93 IPv4 Fig 3 94 IPv4...
Page 128: ...72 Fig 3 95 IPv4 Fig 3 96 IPv4 Fig 3 97 IPv4 Fig 3 98 IPv4 Fig 3 99 IPv4...
Page 129: ...73 Fig 3 100 IPv4 Fig 3 101 IPv4 Fig 3 102 IPv4...
Page 130: ...74 Fig 3 103 IPv4 Fig 3 104 IPv4 Fig 3 105 IPv4...
Page 131: ...75 Fig 3 106 IPv4 Fig 3 107 IPv4 Fig 3 108 IPv4...
Page 132: ...76 Fig 3 109 IPv4 Fig 3 110 IPv4 Fig 3 111 IPv4...
Page 133: ...77 Fig 3 112 IPv4 Fig 3 113 IPv4 Fig 3 114 IPv4...
Page 134: ...78 Fig 3 115 IPv4 Fig 3 116 IPv4 Fig 3 117 Action...
Page 135: ...79 Fig 3 118 Rate Limiter Fig 3 119 Port Copy...
Page 136: ...80 Fig 3 120 DMAC Filter Fig 3 121 VLAN ID Filter Fig 3 122 VLAN ID Filter...
Page 148: ...92 Fig 3 125 Set up Policy Rules Fig 3 126 Set up Policy Rules Fig 3 127 Set up Policy Rules...
Page 150: ...94 Fig 3 131 Set up Port Policies Fig 3 132 Set up Port Policies Finish...
Page 164: ...108 Fig 3 143 802 1X Server Configuration...
Page 168: ...112 Fig 3 145 802 1X Status...
Page 194: ...138 Fig 3 161 Mirror Configuration...
Page 214: ...158 Fig 4 1 Fig 4 2 LGB1005A R2 LGB1005A R2 LGB1005A R2 LGB1005A R2...
















































