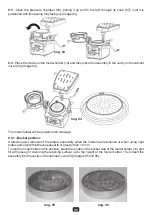
12
9 - MAIN APPLICATIONS
9.1 - FIXATION OF BRACKETS
9.2 - CAPS
9.3 - DIE FOR COMPOSITE RESIN
9.4 - PROVISIONAL BRIDGE
Indicated plates
Indicated plates
Indicated plates
Indicated plates
Ideal laminating point
Ideal laminating point
Ideal laminating point
Ideal laminating point
Finishing
Finishing
Finishing
Finishing
Considerations
Considerations
Considerations
Soft Plate 1.0 mm
Crystal Plate 0.3 mm
Crystal Plate 0.3 mm
Milky Plate 0.6 mm
Soft 2.0 mm.
Milky Plate 0.6 mm
Soft 2.0 mm.
Plate flow
Plate flow
Plate transparency to milky.
Flow to Soft.
Plate transparency to milky.
Flow to Soft.
Use model bucket holder.
Cut out the plate with a utility knife or scissors.
Use a flat model door.
Cut out the plate with a knife, scissors or scalpel.
Use a flat model door.
Cut out the plate with a knife, scissors or scalpel.
Use a flat model door.
Cut out the plate with a knife, scissors or scalpel.
The brackets must be positioned on the study model before
lamination with glue that is not very adherent so that they can be
easily removed together with the plate after lamination.
Next, the patient's teeth are properly prepared and the plate is
placed with the brackets, thus fixing all the brackets at once.
Carefully remove the plaque with a knife or scalpel.
For better use of the plate, several dies can be placed on the
model holder, as long as there is enough space between them for
laminating.
The dies can be placed on the model holder on a mold or
children's colored clay.
Dental reconstruction is performed on the study model with
material that withstands the heating temperature (plaster, resin,
mold, teeth, artificial teeth...). If using wax, a duplicate of the
plaster model must be made, as the wax melts with the heat of the
machine. Use only the indicated material (Milk or Soft plate), as
other types of material may chemically react with the resin.