AUBER INSTRUMENTS
WWW.AUBERINS.COM
2021.05
P3/7
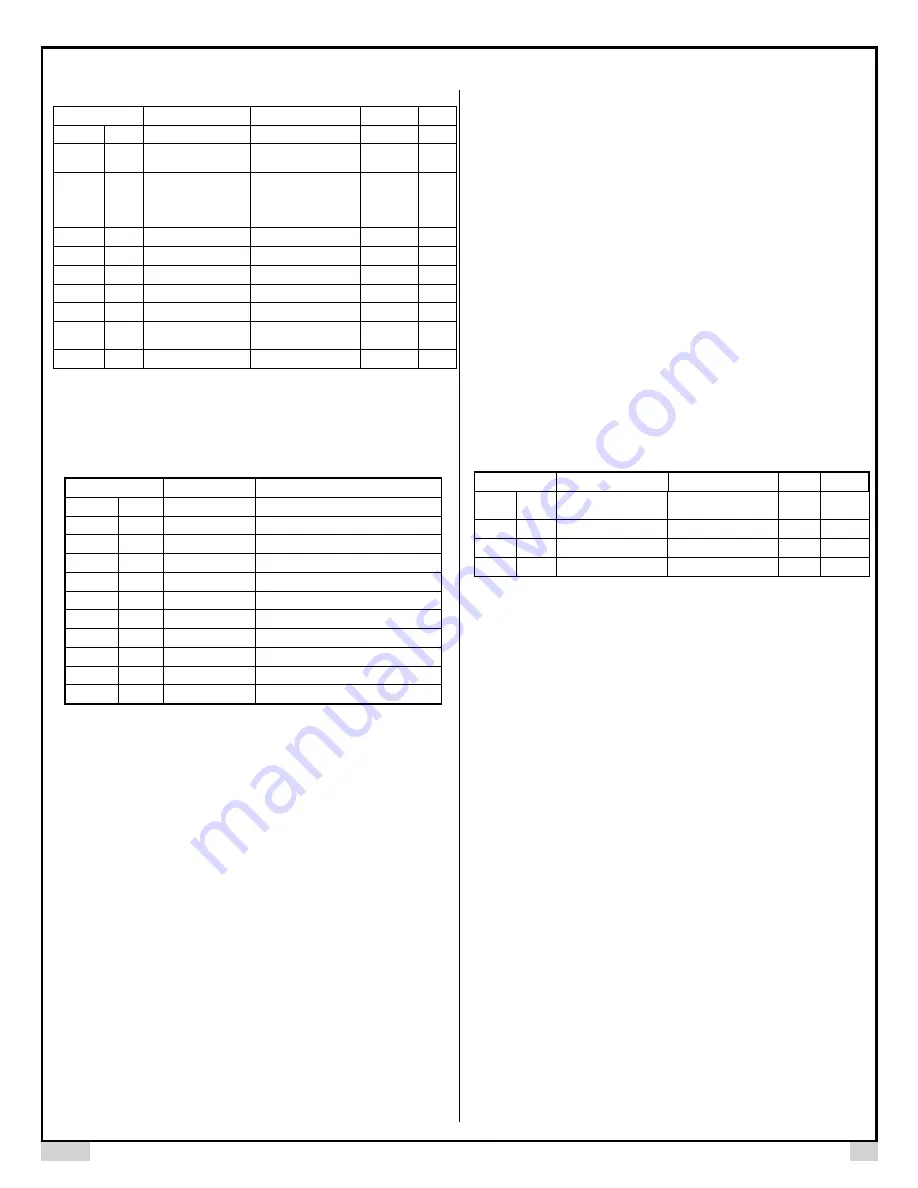
Table 1. System configuration parameters.
Code
Description
Setting Range
Initial
Note
Inty
Inty
Input Sensor Type
See Table 2
K
1
outy
outy
Control Output
Mode
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
1
2
Coty
coty
Main Output Mode
0 - 20 mA,
4 - 20 mA,
SSR (does not apply
to this model)
0 - 20
mA
3
Hy
Hy
Hysteresis Band
0 ~ 9999
3
4
PSb
PSb
Input Offset
-100 ~ 100 (deg.)
0
5
rd
rd
Control Direction
0: heating; 1: cooling
0
CorF
CorF
Display Unit
C, F
F
Id
Id
Unit ID
1 ~ 64
5
6
baud
bAud
Baud Rate
1200, 2400, 4800,
9600
9600
6
End
End
Exit
Note 1.
The controller is preset for K type thermocouple input. If any other type of
sensor is used, the
Inty
value needs to be changed to the corresponding symbol
as shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Temperature sensor code.
Symbol
Description
Working Temperature Range
t
T
TC, Type T
-200 ~ 400° C; -320 ~ 752° F
r
R
TC, Type R
-50 ~ 1600° C; -58 ~ 2900° F
j
J
TC, Type J
-200 ~ 1200° C; -320 ~ 2200° F
WRE
WRe
TC, WRe 3/25
0 ~ 2300° C; 32 ~ 4200° F
b
B
TC, Type B
350 ~ 1800° C; 660 ~ 3300° F
s
S
TC, Type S
-50 ~ 1600° C; -58 ~ 2900° F
k
K
TC, Type K
-200 ~ 1300° C; -320 ~ 2400° F
e
E
TC, Type E
-200 ~ 900° C; -320 ~ 1650° F
P100
P100
RTD, Pt100
-200 ~ 600° C; -320 ~ 1100° F
P10
.
0
P10.0
RTD, Pt100
-99.9 ~ 600.0° C; -99.9 ~ 999.9° F
Cu50
Cu50
RTD, Cu50
-50.0 ~ 150.0° C; -60 ~ 300° F
Note 2.
The setting of
outy
determines the control output mode. When it is set
to:
1 - J1 relay works as absolute alarm output; mA port as PID control output;
2 - J1 relay works as derivation alarm output; mA port as PID control output;
3 - J1 relay works as PID control output; mA port disabled;
4 - J1 relay works as on/off control output; mA port disabled;
5 - J1 relay works as absolute alarm output; mA port disabled.
Note 3.
The setting of
Coty
determines the main output modes on the mA port
(terminal 7 & 8). When it is set to:
“0
-
20”
- Main output is set to 0 - 20 mA linear current output mode.
“4
-
20”
- Main output is set to 4 - 20 mA linear current output mode.
“SSR”
- Not available on SYL-2381-mA.
Note 4.
Hysteresis Band
Hy
(also called dead band, or differential) is used in on/off
control mode. Its unit is in degrees (
°
C or
°
F). When the controller works in on/off
control mode for heating, the output will be off when PV > SV and on again when
PV < (SV - Hy). When the controller works in on/off control model for cooling, the
output will be off when PV < SV and on again when PV > (SV + Hy).
Note 5
. Input offset
PSb
is used to set an input offset to compensate the error
produced by the sensor. For example, if the meter displays 3ºC when probe is in
ice/water mixture, setting
PSb
= -3, will make the controller display 0ºC. To set a
negative value, use Shift (>) key to go to the very left digit, then press Down key
(V) until the first digit change to
“
-
”.
Note 6.
Parameter
ID
and
bAud
are used for RS485 communication. For details,
please check the supplementary manual.
5.2 PID parameters (accessed by code 0036)
The PID control parameters are listed in Table 3. To change the parameters, press
SET key, en
ter code “0036”, and press SET
key again. The operation to change
these parameters is similar to what is shown in the flow chart in Figure 3.
The values of the
P
,
I
, and
D
parameters are critical for good response time,
accuracy, and stability of the system. Using the Auto-tune function to automatically
determine these parameters is recommended for the first-time users. If the auto-
tuning result is not satisfactory, you can manually fine-tune the PID constants for
improved performance.
Table 3. PID parameters.
Symbol
Description
Setting Range
Initial
Note
P
P
Proportional
Constant
0.1 ~ 9999.9
5.0
7
I
I
Integral Time
2 ~ 1999 (sec)
100
8
d
d
Derivative Time
0 ~ 399 (sec)
20
9
End
End
Exit
Note 7.
Proportional Constant (
P
): Also called Proportional Band. Its unit is degree.
If
CorF
is set to ° F, the unit of P is 1° F. If
CorF
is set to ° C, the unit of P is 1° C.
Assuming the set temperature
SV
is set to 200° F, Proportional Constant
P
is set
to 5.0. When integral (
I
) and derivative (
d
) actions are both removed, i.e.,
I
= 0 and
d
= 0, the controller
’s
output should change from 100% to 0% as the temperature
increases from 195° F to 200° F. The smaller the
P
value, the stronger the action
will be for the same amount of temperature difference between
SV
and
PV
.
Note 8.
Integral Time (
I
): Brings the system up to the set value (
SV
) by adding to
the output that is proportional to how far the process value (
PV
) is from the set
value (
SV
) and how long it has been there. When
I
is set to a smaller value, the
response speed is faster but the system is less stable. When
I
is set to a larger
value, the respond speed is slower, but the system is more stable.
Note 9
. Derivative Time (
d
): Responds to the rate of process temperature (PV)
change, so that the controller can compensate in advance before the difference
between
SV
and
PV
(|
SV
-
PV
|) gets too big. A larger
d
value increases its action.
Setting
d
value too small or too large would decrease the stability of the system,
cause oscillation, or even make the system non-convergent.
5.3 Control parameters
The control parameters are listed in Table 4. To change the parameters, press
they
SET key, enter code “0038”,
then press the SET key again. The procedures
to change control parameters are similar to what is shown in Figure 3.

























