For your switch, if you want to build redundant paths between important nodes in your network to provide
some fault tolerance, you should enable Spanning Tree Protocol support on the switch. This ensures that only
one of the redundant paths is active at any time, thus avoiding data path loops. Spanning Tree can be enabled
through the switch console or the web browser interface. For more information on Spanning Tree, see the
Advanced Traffic Management Guide for your switch at
http://www.hpe.com/support/manuals
.
The switch also supports Trunking, which allows multiple network cables to be used for a single network
connection without causing a data path loop. For more information on Trunking, see the Management and
Configuration Guide, which is on the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website at
http://www.hpe.com/support/
manuals
.
•
Faulty or loose cables
: Look for loose or obviously faulty connections. If they appear to be OK, make sure
the connections are snug. If that does not correct the problem, try a different cable.
•
Non-standard cables
: Non-standard and incorrectly-wired cables may cause network collisions and other
network problems, and can seriously impair network performance. A category 5 or greater cable tester is a
recommended tool for every 100Base-TX and 1000Base-T network installation.
•
Check the port configuration
: A port on your switch may not be operating as expected because it is
administratively disabled in the configuration. It may also be placed into a “blocking” state by a protocol
operating on the port (dynamic VLANs), or LACP (dynamic trunking). For example, the normal operation of the
spanning tree, GVRP, LACP, and other features may put the port in a blocking state.
Use the switch console to determine the port’s configuration and verify that there is not an improper or
undesired configuration of any of the switch features that may be affecting the port. For more information, see
Management and Configuration Guide
for your switch at
http://www.hpe.com/support/manuals
.
Diagnosing with the LEDs
LED patterns for general switch troubleshooting
To use the LEDs for general troubleshooting, check the table for the LED pattern you see then refer to the
corresponding diagnostic tip in the next table.
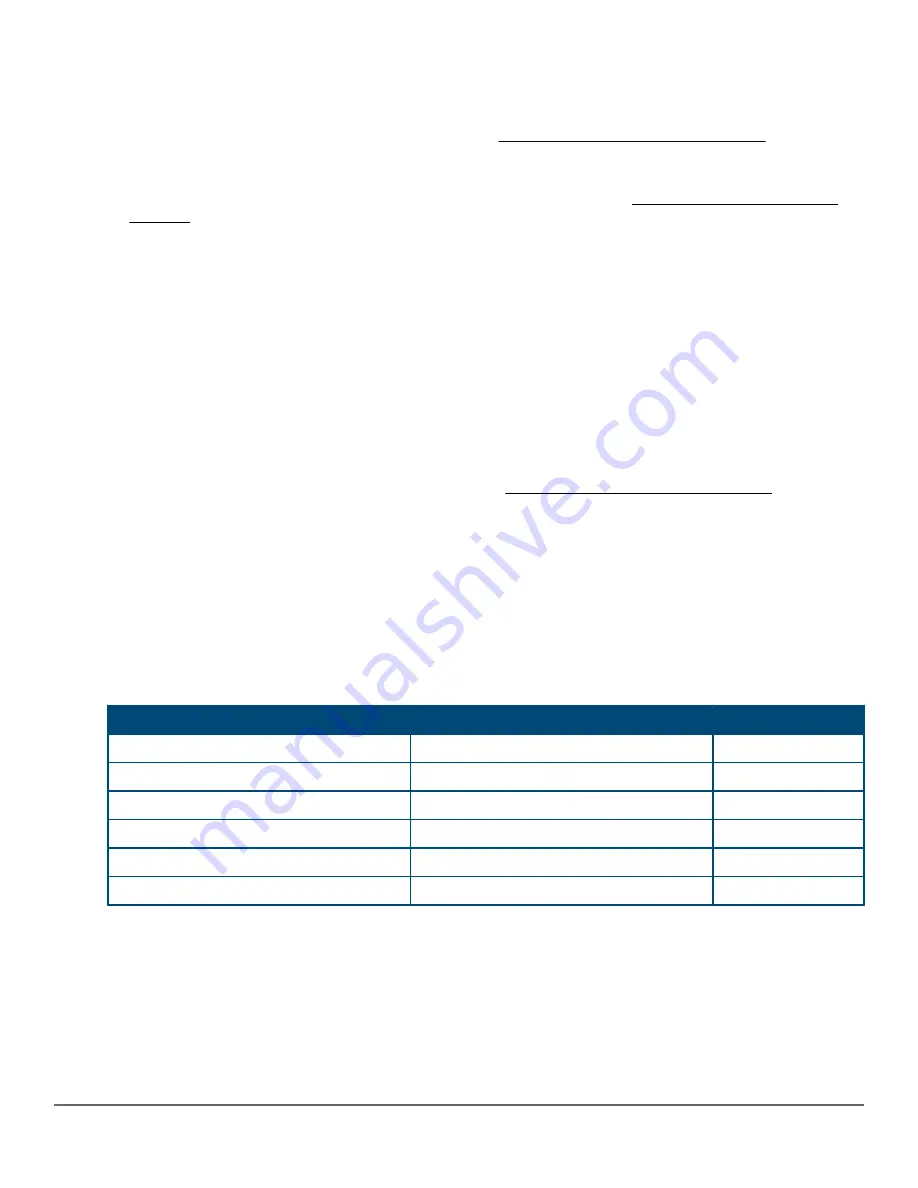
Table 11: LED error indicators
Global status
Port LED
Diagnostic tip
Off with power cord plugged in
1
Solid orange
2
Slow flash orange
3
Slow flash orange
Slow flash orange
1
4
Solid green
Off with cable connected
5
Solid green
On, but the port is not communicating
6
1
The flashing behavior is an on/off cycle once every 1.6 seconds, approximately.
50
Aruba 2930F Switch Series Installation and Getting Started
Guide
















































