9
ST5/10-Si,-Q,-C, IP Hardware manual
920-0004 Rev. C
4/21/11
Connecting the Drive to Your PC using Ethernet
This process requires three steps
• Physically connect the drive to your network (or directly to the PC)
• Set the drive’s IP address
• Set the appropriate networking properties on your PC.
Note: the following pages are an excerpt from the “eSCL Communication Reference Guide”. For more
information, please read the rest of the guide.
Addresses, Subnets, and Ports
Every device on an Ethernet network must have a unique IP address. In order for two devices to communi-
cate with each other, they must both be connected to the network and they must have IP addresses that are
on the same subnet. A subnet is a logical division of a larger network. Members of one subnet are gener-
ally not able to communicate with members of another unless they are connected through special network
equipment (e.g. router). Subnets are defined by the choices of IP addresses and subnet masks.
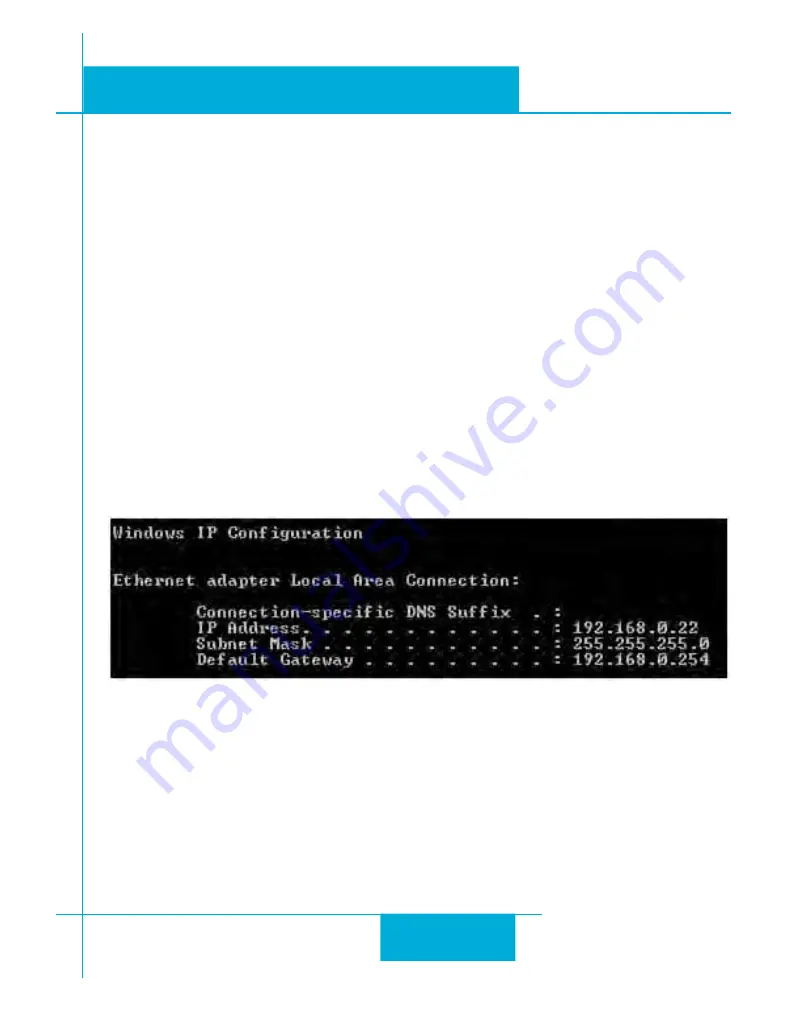
If you want to know the IP address and subnet mask of your PC, select Start…All Programs…Accesso-
ries…Command Prompt. Then type “ipconfig” and press Enter. You should see something like this:
If your PC’s subnet mask is set to 255.255.255.0, a common setting known as a Class C subnet mask, then
your machine can only talk to another network device whose IP address matches yours in the first three
octets. (The numbers between the dots in an IP address are called octets.) For example, if your PC is on a
Class C subnet and has an IP address of 192.168.0.20, it can talk to a device at 192.168.0.40, but not one at
192.168.1.40. If you change your subnet mask to 255.255.0.0 (Class B) you can talk to any device whose
first two octets match yours. Be sure to ask your system administrator before doing this. You network may
be segmented for a reason.
Your drive includes a 16 position rotary switch for setting its IP address. The factory default address for
each switch setting is shown in the table on the next page.
























