Theory of Operation
AQUATRAN 3/38 Operator’s Manual
D-4
Revision G
MOCON, Inc.
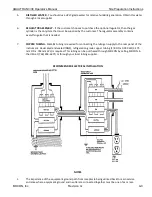
How a Humidified Test Gas is Generated
A Humidified Test Gas is created by moving pressurized gas through a humidifier filled with HPLC-grade
water and mixing the wet gas with a dry gas in the appropriate ratios.
A mixing valve is used to “mix” the saturated gas (~100% RH) with the dry gas. A mix-ratio of 50% yields a
gas with an RH of approximately 50%.
A RH sensor is used to measure the actual RH delivered to the Test Cell. The instrument uses the
measured RH value to adjust the mixture ratio to maintain the RH of the gas delivered at the specified
value.
The RH that the sample will be tested at can be changed by simply changing the RH set point. The
“Sequential Test” feature can be used to automatically perform a sequence of tests at different RH levels.
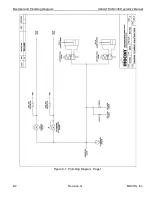
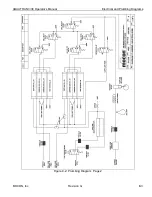
How the ReZero Cell Works
The transmission rate measured for samples mounted in a test cell is the sum of the transmission rate due
to permeation through the barrier material and all other sources of water vapor ingress. This includes the
system baseline. If the system baseline can be measured, subtracting it from the apparent transmission rate
of the test cell will give a more accurate representation for the transmission rate of the barrier material.
During a ReZero State the instrument routes carrier gas (which is at the same temperature as used in the
Test Cells) to the water vapor sensor. The instrument components used to perform this function are referred
to as the ReZero Cell. The ReZero Cell is different from a test cell in that it does not contain a barrier
material that is exposed to a Test Gas. This means that any residual water vapor in the carrier gas is not
due to permeation through the barrier materials mounted in the test cell. The residual water vapor measured
in the ReZero State is therefore considered to be a good representation of the system baseline.
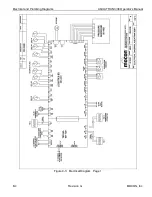
Periodically the instrument baseline is measured using the ReZero Cell. The ReZero Interval and
Examination Time is determined the by currently active Test Method. The resulting data is used to correct
the transmission rate data for any active tests. This ensures that changes in the baseline do not affect the
accuracy of the transmission rate data.