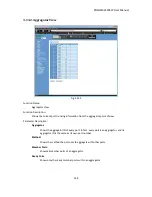
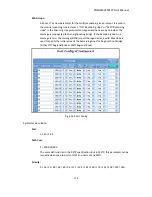
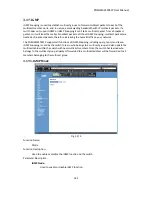
POEGEM24T4SFP
User
Manual
168
more
possible
the
port
will
become
the
root
port.
Configured
Path
Cost:
If
the
path
cost
is
equal
to
zero,
the
path
cost
will
be
auto
‐
negotiated
and
displayed
in
the
path
cost
status
field.
Otherwise
the
value
that
the
administrator
has
set
manually
will
be
displayed.
Valid
range
is
0
–
200,000,000
802.1w
RSTP
recommended
values:
10Mbps:
2,000,000
100Mbps:
200,000
1Gbps:
20,000
Default:
0
Priority:
Indicates
the
port
priority,
the
port
priority
and
port
number
are
mixed
to
form
the
port
ID.
Port
ID’s
are
often
compared
in
order
to
determine
which
port
of
a
bridge
would
become
the
root
port.
Valid
range
is
0
–
240
Default:
128
Admin
Edge
Port:
If
Enabled,
this
port
will
be
an
edge
port.
An
Edge
Port
is
a
port
connected
to
a
device
that
knows
nothing
about
STP
or
RSTP.
Usually,
the
connected
device
is
an
end
station.
Edge
Ports
will
immediately
transit
to
forwarding
state
and
skip
the
listening
and
learning
state
because
edge
ports
cannot
create
bridging
loops
in
the
network.
When
the
link
on
the
edge
port
toggles,
the
STP
topology
stays
unchanged.
Unlike
the
designated
port
or
root
port,
an
edge
port
will
transit
to
a
normal
spanning
‐
tree
port
immediately
if
it
receives
a
BPDU.
Default:
No
Admin
Point
to
Point:
We
say
a
port
is
a
point
‐
to
‐
point
link,
if
it
is
in
full
‐
duplex
mode
but
is
a
shared
link
if
it
is
in
half
‐
duplex
mode.
RSTP’s
fast
convergence
can
only
occur
on
point
‐
to
‐
point
links
and
on
edge
ports.
There
are
three
parameters,
Auto,
True
and
False,
used
to
configure
the
type
of
point
‐
to
‐
point
link.
If
this
parameter
is
configured
as
Auto,
it
means
that
RSTP
will
use
the
duplex
mode
resulting
from
the
auto
‐
negotiation.
In
today’s
switched
networks,
most
links
are
running
in
full
‐
duplex
mode.
If
the
result
is
half
‐
duplex,
then
the
port
will
not
fast
transit
to
Forwarding
state.
If
it
is
set
as
True,
the
port
is
treated
as
a
point
‐
to
‐
point
link
by
RSTP
and
will
be
unconditionally
transited
to
Forwarding
state.
If
it
is
set
as
False,
fast
transition
to
Forwarding
state
will
not
occur
on
this
port.
Default:
Auto
M
Check:
Migration
Check,
forces
the
port
to
send
out
an
RSTP
BPDU
instead
of
a
legacy
STP
BPDU
at
the
next
transmission.
The
only
benefit
of
this
operation
is
to
make
the
port
quickly
act
as
an
RSTP
port.
Click
the
<M
Check>
button
to
send
a
RSTP
BPDU
from
the
port
you
specified.
Summary of Contents for POEGEM24T4SFP
Page 68: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 68 Move to the previous page Next Page Move to the next page...
Page 82: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 82 Fig 3 42 Fig 3 43 Fig 3 44...
Page 89: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 89 Fig 3 48...
Page 106: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 106 Fig 3 71 Fig 3 72...
Page 108: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 108 Fig 3 75 Fig 3 76 Fig 3 77 ARP...
Page 109: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 109 Fig 3 78 ARP Fig 3 79 ARP Fig 3 80 ARP Fig 3 81 ARP...
Page 110: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 110 Fig 3 82 ARP Fig 3 83 ARP Fig 3 84 ARP Fig 3 85 ARP...
Page 111: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 111 Fig 3 86 ARP Fig 3 87 ARP Fig 3 88 ARP Fig 3 89 ARP Fig 3 90 ARP...
Page 112: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 112 Fig 3 91 IPv4 Fig 3 92 IPv4 Fig 3 93 IPv4...
Page 115: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 115 Fig 3 105 IPv4 Fig 3 106 IPv4 Fig 3 107 IPv4...
Page 116: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 116 Fig 3 108 IPv4 Fig 3 109 IPv4 Fig 3 110 IPv4...
Page 117: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 117 Fig 3 111 IPv4 Fig 3 112 IPv4 Fig 3 113 IPv4 Fig 3 114 IPv4...
Page 118: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 118 Fig 3 115 IPv4 Fig 3 116 IPv4 Fig 3 117 IPv4...
Page 119: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 119 Fig 3 118 IPv4 Fig 3 119 IPv4 Fig 3 120 IPv4...
Page 120: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 120 Fig 3 121 Action Fig 3 122 Rate Limiter...
Page 121: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 121 Fig 3 123 Port Copy Fig 3 124 DMAC Filter...
Page 211: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 211 Fig 4 3...
Page 238: ...POEGEM24T4SFP User Manual 238 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 POEGEM24T4SFP acl...