Functions
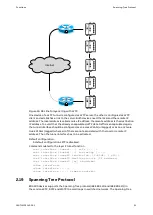
Serial Tunnel
Tunnel groups can be defined to separate logically different data streams in the same
network. Only endpoints with the same tunnel group transmit serial data streams among
each other. Up to ten different tunnel groups can be set.
There is forward error correction. This can be deactivated by setting transmission mode
to fast. If the forward error correction is activated then the loss of single packets in the
Ethernet/IP network does not lead to interruption of the serial data stream, yet, twice the
bandwidth is required.
The default value for transmission mode is fail-safe (forward error correction enabled).
A source VLAN can be defined to bind the data transmission of the serial tunnel to a certain
VLAN (and therefore the IP address of the VLAN interface). This leads to a clean separation of
the data traffic.
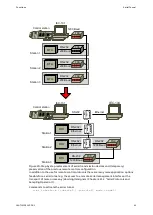
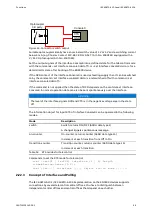
Commands for the configuration of topology and transmission of the serial tunnel
< s e t i n t e r f a c e { c o n s o l e 0 | c o n s o l e 1 } i p - t a r g e t { I P
< c l e a r i n t e r f a c e { c o n s o l e 0 | c o n s o l e 1 } i p - t a r g e t { I P
| f a s t | l o c a l - o n l y } >
< s e t i n t e r f a c e c o n s o l e s o u r c e v l a n { 1 - 4 0 9 4 } >
2.21.4
Enhanced Parameters of the Serial Tunnel
The default values work for many applications without the need of an enhanced configuration
via the serial interface settings (refer to Chapter 2.20.2, "Transmission Parameters of the
Interface") and the basic settings of the serial tunnel (Tunnel mode, IP targets, Tunnel Group).
There are further settings for protocols that react delicately to changes in timing to minimize
the effects of the transport through the Ethernet/IP network. In general the requirements are
very different so that for each individual case the suitable setting has to be found.
The sampling frequency determines how often the registered serial data is sent via the
Ethernet/IP network. This setting has influence on the required bandwidth for tunnelling and
the delay of the serial data stream. The lower the "sampling frequency" the more bandwidth
is required but the lower the delay of the data.
The default value for sampling is: 20 ms.
Depending on the applied baud rate the frequency can be set to values between 120 ms (for
low baud rates) down to 1 ms (values below 10 ms should be used only in exceptional cases as
the resulting network load rises out of proportion).
Caused by the sampling frequency and timing effects it can happen that serial telegrams
that reach the tunnel entrance in one piece, disintegrate in respect to time into several pieces
(separate bytes) at the tunnel exit. This can be critical depending on the application.
1KGT151021
V000 1
63