10-4
C
HAPTER
10: FDDI N
ETWORKS
This means that subsets of legal topologies are also legal. Examples of legal
FDDI topologies include the dual ring with trees, the dual ring without
trees, and the single tree. For information on legal topologies, see the
section “FDDI Connection Rules” later in this chapter.
Logical Topology:
The Dual Ring
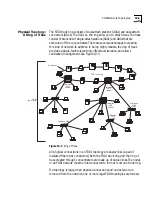
A legal FDDI topology consists of at most two separate logical rings: the
primary ring and the secondary ring. These logical rings are formed from
the physical links that make up the Physical Layer connections. For example,
a set of DASs connected into a closed loop form an FDDI dual ring. Each
ring is a logical ring, that is, a separate data path with its own token.
Functionally, one of the major characteristics of the FDDI network is its dual
ring, which provides a high degree of reliability to a LAN. When an FDDI
network is in normal operation, only the primary ring is used to transmit
and receive data. The secondary ring may also be used to carry data, but it
is typically used as a backup in case there is a connectivity problem in the
primary ring or in one of the nodes on the ring.
When a single fault takes place on an FDDI dual ring, recovery can be made
by joining the two rings between the two nodes adjacent to the fault. This
creates a single logical ring resulting in a wrapped configuration. A wrapped
ring is a legal FDDI topology. In the same way, when many faults take place,
several disjointed logical rings are created, producing multiple FDDI
topologies.
FDDI Connection
Rules
Station Management Protocol (SMT) follows specific connection rules to
ensure that only desired physical connection types are included in the
LANplex network topology. A connection’s
type
is determined by the types
of the ports at either end of the connection. There are three categories of
connection types:
■
valid
— Always accepted
■
illegal
— Always rejected
■
undesired
— Either accepted or rejected as determined by connection
policies established by the network manager
SMT notifies network management software when undesired connection
types are attempted, regardless of whether the connection is accepted or
Summary of Contents for LANPLEX 2500
Page 1: ...LANPLEX 2500 OPERATION GUIDE Part No 801 00344 000 Published November 1996 Revision 03...
Page 14: ......
Page 18: ...1 4 CHAPTER 1 LANPLEX MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION OVERVIEW...
Page 78: ...III Chapter 9 FDDI Overview and Implementation Chapter 10 FDDI Networks FDDI TECHNOLOGY...
Page 97: ...IV Chapter 11 ATM Networks ATM TECHNOLOGY...
Page 116: ...V Appendix A SNMP MIB Support Appendix B Technical Support APPENDIXES...