Spanning Tree and the Bridged Network
5-9
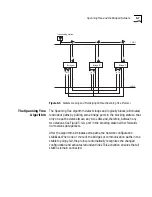
receiving information. Figure 5-5 shows the hierarchy of the Spanning Tree
bridges and their ports.
Figure 5-5
Hierarchy of the Root Bridge and the Designated Bridge
From the information that the CBPDUs provide, the bridges:
■
Elect a single bridge to be the
root
bridge
. The root bridge has the lowest
bridge ID among all the bridges on the extended network.
■
Calculate the best path between themselves and the root bridge.
■
Elect a
designated bridge
on each LAN from among the bridges residing
on that LAN. This is the bridge with the least cost path to the root bridge.
Its function is to forward packets between that LAN and the path to the
root bridge. For this reason, the root bridge is
always
the designated bridge
for its attached LANs. The port through which the designated bridge is
attached to the LAN is elected the
designated port.
■
Choose a
root port
that gives the best path from themselves to the root
bridge.
■
Select ports to be included in the Spanning Tree topology. The ports
selected include the root port plus any designated ports. Data traffic is
forwarded to and from ports selected for inclusion in the Spanning Tree
topology. Data traffic is never forwarded to or received on ports that are not
selected for inclusion in the Spanning Tree topology.
Root port
Designated port
Root Bridge
Designated
Bridge
Root port
Designated port
Bridge
Summary of Contents for LANPLEX 2500
Page 1: ...LANPLEX 2500 OPERATION GUIDE Part No 801 00344 000 Published November 1996 Revision 03...
Page 14: ......
Page 18: ...1 4 CHAPTER 1 LANPLEX MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION OVERVIEW...
Page 78: ...III Chapter 9 FDDI Overview and Implementation Chapter 10 FDDI Networks FDDI TECHNOLOGY...
Page 97: ...IV Chapter 11 ATM Networks ATM TECHNOLOGY...
Page 116: ...V Appendix A SNMP MIB Support Appendix B Technical Support APPENDIXES...