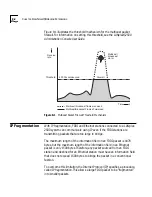
Paths
9-5
Paths
FDDI’s dual, counter-rotating ring is made up of a primary and secondary
ring. FDDI stations can be connected to either ring or to both rings
simultaneously. Data flows downstream on the primary ring in one direction
from one station to its neighboring station. The secondary ring serves as a
redundant path and flows in the opposite direction. When a link or station
failure occurs, the ring “wraps” around the location of the failure, creating a
single logical ring.
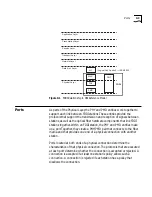
Paths represent the segments of a logical ring that pass through a station.
An FDDI station can contain three paths:
■
Primary path
—
The segment or segments of the primary ring that pass
through a station. Conditions may exist in parts of the network that might
cause the path to be in a different ring. The primary path must be present in
all nodes on the network.
■
Secondary path
—
The segment or segments of the secondary ring that
pass through a station. Conditions may exist in parts of the network that
may cause the path to be in a different ring.
■
Local path
—
One or more segments of the rings other than the primary
ring and secondary ring that pass through the station.
Nodes and
Attachments
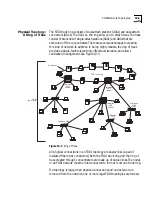
As we have seen, an FDDI network is made up of stations and concentrators
that contain active services or management elements that conform to the
ANSI FDDI standards. These stations and concentrators are connected to
optical fiber medium and are attached in the prescribed manner set forth in
the FDDI standards to allow reliable data transmission. Connections are
made through FDDI ports and are managed by FDDI MACs.
Nodes
An FDDI network is made up of logically connected
nodes
.
This
generic
term is used to refer to any active
station
or
concentrator
in an FDDI
network.
■
A
station
is any addressable node on an FDDI network that can transmit,
repeat, and receive information. A station contains
only
one SMT, and
at
least one
MAC, one PHY, and one PMD.
■
A
concentrator
is an FDDI station with additional PHY/PMD entities, beyond
those required for its own connection to an FDDI network. These additional
Summary of Contents for LANPLEX 2500
Page 1: ...LANPLEX 2500 OPERATION GUIDE Part No 801 00344 000 Published November 1996 Revision 03...
Page 14: ......
Page 18: ...1 4 CHAPTER 1 LANPLEX MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION OVERVIEW...
Page 78: ...III Chapter 9 FDDI Overview and Implementation Chapter 10 FDDI Networks FDDI TECHNOLOGY...
Page 97: ...IV Chapter 11 ATM Networks ATM TECHNOLOGY...
Page 116: ...V Appendix A SNMP MIB Support Appendix B Technical Support APPENDIXES...