90
C
HAPTER
6: S
PANNING
T
REE
P
ROTOCOL
(STP)
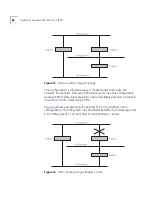
The Root Bridge generates BPDUs on all ports at a regular interval known
as the Hello Time. All other bridges in the network have a Root Port. This
is the port that costs the least in getting to the Root Bridge, and it is used
for receiving the BPDUs initiated by the Root Bridge.
Stabilization
After all bridges on the network have determined the configuration of
their ports, each bridge only forwards traffic between the Root Port and
the ports that are the Designated Bridge Ports for each network segment
to which they are attached. All other ports are
blocked
, which means that
they are prevented from forwarding traffic.
Reconfiguration
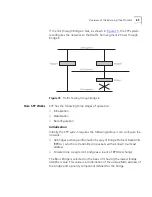
In the event of a network failure (such as a segment going down) the STP
system reconfigures the network to adjust for the changes. If the
topology of the network changes, the Root Bridge sends out an SNMP
trap.
Spanning Tree
Domains
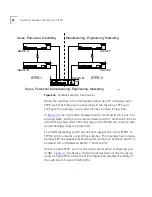
The switch can be partitioned into multiple virtual bridges. Each virtual
bridge can run an independent Spanning Tree instance. Each Spanning
Tree instance is called a
Spanning Tree Domain
(STPD). Each STPD has its
own Root Bridge and active path. Once the STPD is created, one or more
VLANs can be assigned to it.
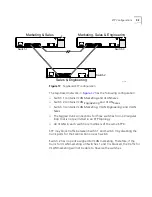
A port can belong to only one STPD. If a port is a member of multiple
VLANs, then all those VLANs must belong to the same STPD.
The key points to remember when configuring VLANs and STP are the
following:
■
Each VLAN forms an independent broadcast domain.
■
STP blocks paths to create a loop-free environment.
■
When STP blocks a path, no data can be transmitted or received on
the blocked port.
■
Within any given STPD, all VLANs belonging to it use the same
spanning tree.
Summary of Contents for 3C17705
Page 10: ...GLOSSARY INDEX INDEX OF COMMANDS 3COM CORPORATION LIMITED WARRANTY EMC STATEMENTS ...
Page 14: ...14 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Page 32: ...32 CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION AND SETUP ...
Page 62: ...62 CHAPTER 3 ACCESSING THE SWITCH ...
Page 80: ...80 CHAPTER 4 VIRTUAL LANS VLANS ...
Page 86: ...86 CHAPTER 5 FORWARDING DATABASE FDB ...
Page 98: ...98 CHAPTER 6 SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL STP ...
Page 110: ...110 CHAPTER 7 QUALITY OF SERVICE QOS ...
Page 124: ...124 CHAPTER 8 STATUS MONITORING AND STATISTICS ...
Page 130: ...130 CHAPTER 9 USING THE WEB INTERFACE ...
Page 136: ...136 CHAPTER 10 SOFTWARE UPGRADE AND BOOT OPTIONS ...
Page 156: ...156 APPENDIX C TROUBLESHOOTING ...
Page 162: ......
Page 176: ...176 INDEX ...
Page 180: ...180 INDEX OF COMMANDS ...