Appendix C Wireless LANs
NBG-510S User’s Guide
190
Encryption
Both WPA and WPA2 improve data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. WPA and WPA2 use Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode with Cipher block chaining Message
authentication code Protocol (CCMP) to offer stronger encryption than TKIP.
TKIP uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by the authentication
server. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a block cipher that uses a 256-bit
mathematical algorithm called Rijndael. They both include a per-packet key mixing function,
a Message Integrity Check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with
sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism.
WPA and WPA2 regularly change and rotate the encryption keys so that the same encryption
key is never used twice.
The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up
a key hierarchy and management system, using the PMK to dynamically generate unique data
encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP
and the wireless clients. This all happens in the background automatically.
The Message Integrity Check (MIC) is designed to prevent an attacker from capturing data
packets, altering them and resending them. The MIC provides a strong mathematical function
in which the receiver and the transmitter each compute and then compare the MIC. If they do
not match, it is assumed that the data has been tampered with and the packet is dropped.
By generating unique data encryption keys for every data packet and by creating an integrity
checking mechanism (MIC), with TKIP and AES it is more difficult to decrypt data on a Wi-Fi
network than WEP and difficult for an intruder to break into the network.
The encryption mechanisms used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same. The only
difference between the two is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common password, instead of
user-specific credentials. The common-password approach makes WPA(2)-PSK susceptible to
brute-force password-guessing attacks but it’s still an improvement over WEP as it employs a
consistent, single, alphanumeric password to derive a PMK which is used to generate unique
temporal encryption keys. This prevent all wireless devices sharing the same encryption keys.
(a weakness of WEP)
User Authentication
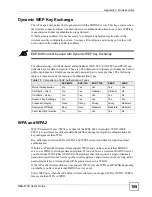
WPA and WPA2 apply IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to
authenticate wireless clients using an external RADIUS database. WPA2 reduces the number
of key exchange messages from six to four (CCMP 4-way handshake) and shortens the time
required to connect to a network. Other WPA2 authentication features that are different from
WPA include key caching and pre-authentication. These two features are optional and may not
be supported in all wireless devices.
Key caching allows a wireless client to store the PMK it derived through a successful
authentication with an AP. The wireless client uses the PMK when it tries to connect to the
same AP and does not need to go with the authentication process again.
Pre-authentication enables fast roaming by allowing the wireless client (already connecting to
an AP) to perform IEEE 802.1x authentication with another AP before connecting to it.
Содержание NBG-510S
Страница 2: ......
Страница 7: ...Safety Warnings NBG 510S User s Guide 7 This product is recyclable Dispose of it properly ...
Страница 8: ...Safety Warnings NBG 510S User s Guide 8 ...
Страница 10: ...Contents Overview NBG 510S User s Guide 10 Troubleshooting and Appendices 163 Troubleshooting 165 ...
Страница 18: ...Table of Contents NBG 510S User s Guide 18 ...
Страница 26: ...26 ...
Страница 44: ...Chapter 5 Setup Wizard NBG 510S User s Guide 44 Figure 20 Wizard Applying Internet Settings ...
Страница 58: ...Chapter 6 Tutorials NBG 510S User s Guide 58 ...
Страница 59: ...59 PART II Network Wireless LAN 61 WAN 69 LAN 77 DHCP 79 NAT and Firewall WAN to LAN 81 DDNS 89 ...
Страница 60: ...60 ...
Страница 76: ...Chapter 8 WAN NBG 510S User s Guide 76 ...
Страница 78: ...Chapter 9 LAN NBG 510S User s Guide 78 ...
Страница 88: ...Chapter 11 NAT and Firewall WAN to LAN NBG 510S User s Guide 88 ...
Страница 91: ...91 PART III Security Access Control 93 Content Filtering 101 ...
Страница 92: ...92 ...
Страница 100: ...Chapter 13 Access Control NBG 510S User s Guide 100 ...
Страница 103: ...103 PART IV Management UPnP 105 Static Route 113 ...
Страница 104: ...104 ...
Страница 116: ...Chapter 16 Static Route NBG 510S User s Guide 116 ...
Страница 117: ...117 PART V Maintenance System 119 Logs 123 Tools 125 ...
Страница 118: ...118 ...
Страница 134: ...134 ...
Страница 136: ...Chapter 20 Secure Remote Access Title NBG 510S User s Guide 136 ...
Страница 140: ...Chapter 21 Secure Remote Access User Info NBG 510S User s Guide 140 ...
Страница 150: ...Chapter 23 Manage User Access Permissions NBG 510S User s Guide 150 ...
Страница 154: ...Chapter 24 Secure Remote Desktop Control NBG 510S User s Guide 154 ...
Страница 162: ...Chapter 25 Secure Remote Access Screens NBG 510S User s Guide 162 ...
Страница 164: ...164 ...
Страница 170: ...Chapter 26 Troubleshooting NBG 510S User s Guide 170 ...
Страница 176: ...Appendix A Product Specifications NBG 510S User s Guide 176 ...
Страница 180: ...Appendix B Common Services NBG 510S User s Guide 180 ...
Страница 198: ...Appendix D Legal Information NBG 510S User s Guide 198 ...
Страница 204: ...Appendix E Customer Support NBG 510S User s Guide 204 ...
Страница 209: ...Index NBG 510S User s Guide 209 WPA PSK 189 190 application example 191 ...
Страница 210: ...Index NBG 510S User s Guide 210 ...