WQG-10029-01
Calibrating D/A Converter
The D/A converter is factory set to the specified
frequency (noted on the label affixed to main
circuit board) and field recalibration is usually not
required. If it becomes necessary to recalibrate the
D/A converter, the following procedure must be
followed and high quality test equipment used. Any
component changes must be made with equivalent
components.
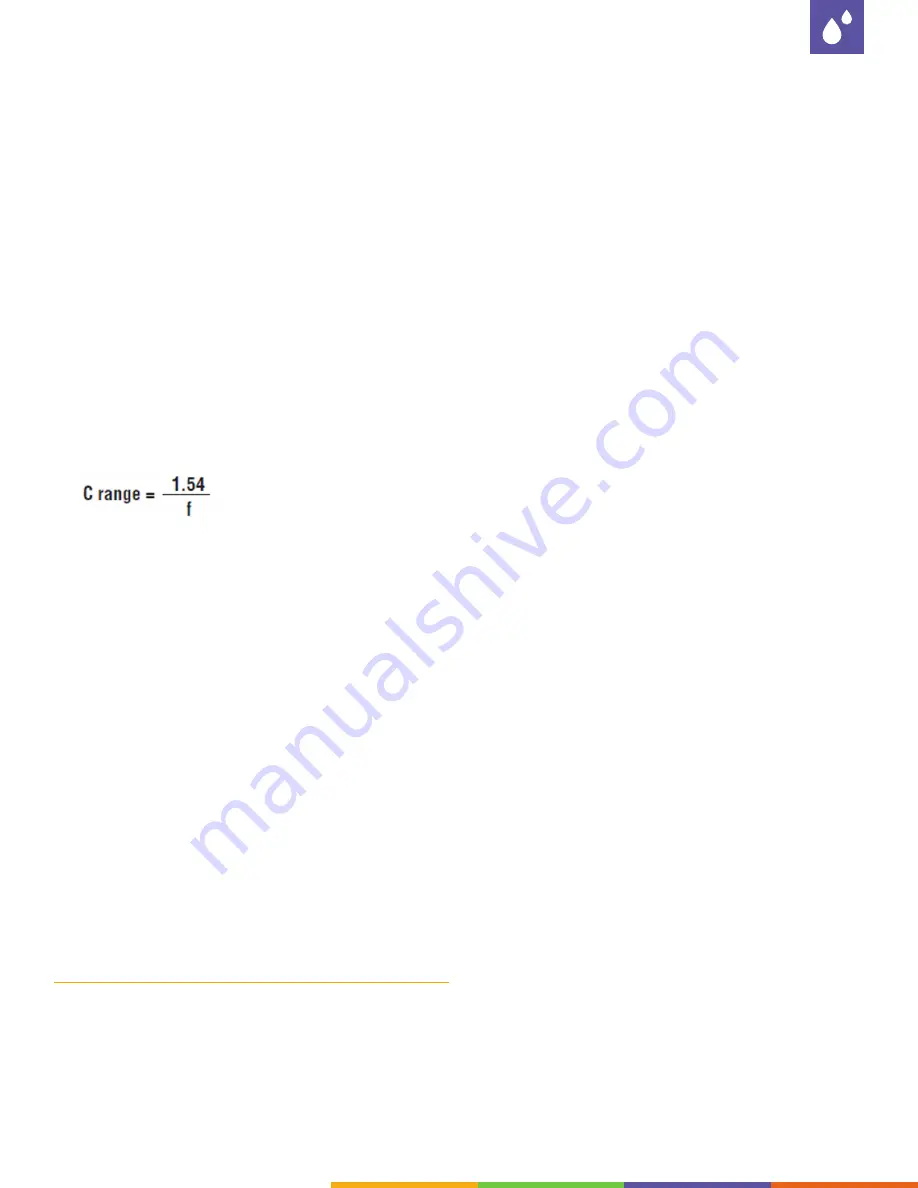
Calculating the RANGE capacitor’s value
To change the input frequency, the range capacitor
may have to be replaced.
Use the formula to determine the necessary value.
For example, to obtain full scale DC output of 20
ma DC at a full scale input pulse rate of 10 pulses/
second, a capacitor of .15 MF is needed. The
stability of the range capacitor affects the stability
of the converter; only polycarbonate or polystyrene
capacitors should be used. The zero and range
potentiometers provide a minimum adjustment
range of + or -10% to accommodate capacitor
tolerances (for the main output).
Test Equipment Setup
Connect signal source onto Act-Pak terminals
#16 and #14, positive and ground respectively.
Signal sources may be solid state or switch driven.
Regardless of the device being used, it must
develop a square wave capable of sinking 50 mA
and interrupting 50 volts. To determine the precise
input frequency, it is suggested that a digital counter
also be connected to terminals #16 and #14.
t
WARNING!
ELECTRICAL HAZARD. Use caution when working with
disassembled AC electrical components.
Act-Pak® Electronic Instrumentation
Models 1100D and 1100DN Quick Guide
Calibration: Proportional Output (4-20 mA) with a
Voltmeter
1. Connect a load resistor across terminals #5 (+) and
#6 (-).
2. This resistor may be of any value less than or equal
to 500 ohms.
3. Connect a digital voltmeter across terminals #5 (+)
and #6 (-)
4. Apply power to the instrument with the signal
source off. The analog output signal should be 4
mA indicated by a 2.0 volt reading if a 500 ohm
load resistor is used.
5. Adjust the ZERO potentiometer, if necessary.
6. Turn on signal source and adjust to full scale input
frequency.
7. Adjust the SPAN potentiometer to obtain a 10.0
volt reading on the voltmeter.
8. If SPAN adjustment is required, repeat step
“c” to check the zero setting; adjust and reset,
if necessary. Each time the ZERO or SPAN
potentiometers are moved, the opposite setting
must be checked until no adjustment is required.
Calibration: Proportional Output (4-20 mA) with a
Milliampere Meter
1. Remove all connections on terminals #5 (+) and #6
(–).
2. Connect a milliampere meter across terminals #5
(+) | and #6 (–).
3. Apply power to the instrument with the signal
source off. The analog output should be 4.0 mA.
4. Adjust the ZERO potentiometer if necessary.
5. Turn on the signal source and adjust to full scale
input frequency.
6. Adjust the SPAN potentiometer to obtain a 20 mA
reading.
7. If SPAN adjustment is required, repeat step
“c” to check the zero setting; adjust and reset,
if necessary. Each time the ZERO or SPAN
potentiometers are moved, the opposite setting
must be checked until no adjustment is required.







