Marine Installation Manual
2021-08
4-44
4 Ancillary Systems
4.4 Fuel gas system
X72DF
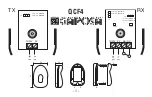
Figure 4
-
25 Pressurised Type C tank solution with NBOG handling by the gensets and
the main engine
Non-pressurised FGSS
For larger LNGCs it is more common to use non-pressurised cargo tanks, there
-
fore the NBOG management must ensure that the pressure build-up does not ex
-
ceed the tank design limits during bunkering and sea voyages. Like in a
pressurised FGSS, a non-pressurised FGSS can combine both FBOG and NBOG
to fuel the main engine(s) and gensets as required. In addition, a re-liquefaction
system can be added as shown in
. This allows for surplus NBOG to
be returned to the tank in liquid form and ensures that the pressure in the FGSS
will not exceed the limits.
Figure 4
-
26 Non-pressurised tank solution, drawn for an LNGC
SM-0684
BOG
LNG
GVU
GVU
GVU
iGPR/GVU
Emergency pressure release
From the bunkering station
Pre-heater
NBOG compressor
Low-pressure vaporiser
Up to 16 bar(g)
Cryogenic
submerged pump
Type C tank
Mostly for LNG-fuelled
vessels and small LNGCs
Gas-fuelled genset
X-DF
main
engine
Gas-fuelled genset
Gas-fuelled genset
Gas supply to
gas-fired boiler
e.g. up to 6 bar(g)
up to 16 bar(g)
e.g. up to 0.3 bar(g)
Pressurised Type C tank solution
with NBOG handling by
the gensets and the main engine
SM-0683
LNGC
GVU
GVU
GVU
iGPR/GVU
LNG tank
LNG tank
LNG tank
Non-pressurised tank solution,
drawn for an LNGC
Re-liquefaction
system
(optional)
Type A tank, Type B tank,
or Membrane tank
Cryogenic submerged pump
GCU
Multi-stage low-pressure
centrifugal, screw or
piston compressor(s)
Low-pressure vaporiser
Up to 16 bar(g)
Gas-fuelled genset
X-DF
main
engine
Gas-fuelled genset
Gas-fuelled genset
Gas supply to
gas-fired boiler
e.g. up to 6 bar(g)
up to 16 bar(g)
e.g. up to 0.3 bar(g)
NBOG