Personal aXsGUARD - 7.7.1
Chapter 3. Features and Concepts
© VASCO Data Security 2013
8
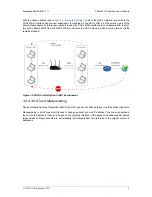
should be connected to the PAX. A secure option is to connect the Internet Interface of the PAX to the
user’s LAN and only connect the client computers that actually need access to corporate resources to the
PAX LAN (double NAT).
For additional information about aXsGUARD Gatekeeper Firewall Rules and Policies, see the
aXsGUARD Gatekeeper Firewall How To, which can be accessed via the Documentation button in the
Administration Tool.
3.4. NAT Traversal
3.4.1. Purpose and Definition
The PAX enables you to easily connect peers that are connected to a Network Address Translated network
segment of a gateway.
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a general term to describe techniques that establish and maintain TCP/
IP and/or UDP connections traversing network address translation (NAT) gateways. For detailed information
about NAT, see the aXsGUARD Gatekeeper System Administration How To, which can be accessed via the
Documentation button in the Administrator Tool.
As of PAX version 1.1, you can configure custom NAT rules on the aXsGUARD Gatekeeper. The rules are
downloaded by the PAX when it connects to the aXsGUARD Gatekeeper VPN server. By default, the NAT
rules apply to the PAX’s WAN interface; they are comparable to port forwarding rules on the aXsGUARD
Gatekeeper.
3.4.2. UPnP and NAT-PMP
Universal Plug and Play and NAT-PMP:
UPnP
(Universal Plug’n'Play) enables programs running on a host to automatically configure port forwarding
on the PAX. UPnP basically allows a program to open ports that are necessary for its operation, without any
warning or intervention from the system administrator. For this reason, there is a security risk associated with
enabling UPnP on the PAX. Technically, a worm or malware could use this function to compromise your LAN’s
security.
It is therefore recommended to manually configure port forwarding whenever possible and disable UPnP.
However, in some cases dynamic port forwarding may be required if manual port forwarding becomes
impractical.
NAT-PMP
is a protocol similar to UPnP supported by a number of Windows and Linux applications.
3.4.3. DNAT and Port Forwarding
Destination network address translation (DNAT) is a technique for transparently changing the destination IP
address of an en route packet and performing the inverse function for any replies. DNAT is commonly used
to publish a service located in a private network on a publicly accessible IP address. This use of DNAT is
also called port forwarding.
In most cases the WAN interface of the PAX is connected directly to the Internet and is assigned a public IP
address. In that case, network packets leaving the WAN interface are masqueraded. (For information about
masquerading, see the aXsGUARD Gatekeeper System Administration How To, which can be accessed
via the Documentation button in the Administrator Tool). By default, the PAX firewall blocks all connections
originating from the Internet.
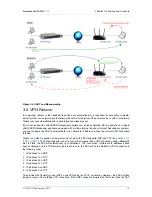
If the WAN interface of the PAX is connected to a NAT’d network in a private range (the WAN interface is
connected to the LAN, as shown in
Figure 3.3, “WAN to LAN Option in NAT Environment”
), you can enable
access to its LAN from the network connected to its WAN interface.