aXsGUARD Identifier 3.0.2.0 Product Guide v1.5
Logging
9
Logging
9.1
Overview
There are two separate sources of information generated on the aXsGUARD Identifier:
Reporting and Auditing: this is the information generated about events in the IDENTIKEY component and
includes amongst others, information about administration events, and authentication attempts. An example
event might be: 'User successfully authenticated'. (Future versions of the aXsGUARD Identifier will also
generate events on electronic signatures and provisioning.) Auditing is explained in section
. Reporting is
explained in section
Logging: this is the information generated about events in the Convenience Layer (see section
includes information about functionalities such as updating, backup and restore. An example log line might be:
'Backup was created successfully'. We explain logging in this section.
Logging is based on the syslog utility which supports local and remote storage and processing of logs. Settings can
be configured in the Configuration Tool manually or using the Configuration Wizard (see section
9.2
Infrastructure
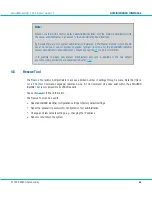
Image 17: Data Transmission from the Syslog Utility to the Live Log Viewer and Remote Syslog
Each component of the Convenience Layer on the aXsGUARD Identifier sends information to the syslog.
('Syslog'
is
a standard log message system on a Linux server and can forward log messages in an IP network.) The syslog
utility handles the information, which can be stored locally or remotely. Both are possible at the same time. Local
logging is always active and cannot be disabled. Syslog data is made available in the live log viewer. Remote
syslog can be activated and needs configuration.
The syslog audit levels are configured through the aXsGUARD Identifier Configuration Tool (see table below).
©
2009 VASCO Data Security
67