Registers
www.ti.com
3.3
Interrupt Enable Register (IER)
The interrupt enable register (IER) is used to individually enable or disable each type of interrupt request
that can be generated by the UART. Each interrupt request that is enabled in IER is forwarded to the
CPU. IER is shown in
Figure 11
and described in
Table 9
.
Access considerations:
IER and DLH share one address. To read or modify IER, write 0 to the DLAB bit in LCR. When DLAB = 1,
all accesses at the shared address read or modify DLH.
DLH also has a dedicated address. If you use the dedicated address, you can keep DLAB = 0, so that IER
is always selected at the shared address.
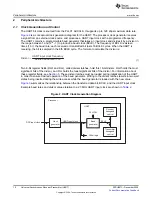
Figure 11. Interrupt Enable Register (IER)
31
16
Reserved
R-0
15
4
3
2
1
0
Reserved
Rsvd
ELSI
ETBEI
ERBI
R-0
R/W-0
R/W-0
R/W-0
R/W-0
LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset
Table 9. Interrupt Enable Register (IER) Field Descriptions
Bit
Field
Value
Description
31-4
Reserved
0
Reserved
3
Reserved
0
Reserved. This bit must always be written with a 0.
2
ELSI
Receiver line status interrupt enable.
0
Receiver line status interrupt is disabled.
1
Receiver line status interrupt is enabled.
1
ETBEI
Transmitter holding register empty interrupt enable.
0
Transmitter holding register empty interrupt is disabled.
1
Transmitter holding register empty interrupt is enabled.
0
ERBI
Receiver data available interrupt and character timeout indication interrupt enable.
0
Receiver data available interrupt and character timeout indication interrupt is disabled.
1
Receiver data available interrupt and character timeout indication interrupt is enabled.
24
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
SPRU997C – December 2009
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated