Glossary 1
GLOSSARY
ANSI
(AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD INSTITUTE)
A group of committees formed to establish voluntary commercial and government standard. ANSI is a member of
ISO.
AT BUS
The AT bus is the ISA bus. It is a 16-bit electronic path containing active signals and power lines to interface with
compatible interfaces or adapter cards for the transfer of data. Data is exchanged 8 or 16-bit at a time (per access) in
parallel.
BIOS
(BASIC INPUT/OUTPUT SYSTEM)
BIOS is permanent built-in firmware that controls accesses to devices that are connected to the computer, such as the
memory, the monitor, the disk drives, the serial communications port, etc. In TEKNOR single board computer, this
may include video BIOS, TEKNOR's BIOS extension, main BIOS and Flat Panel BIOS.
CMOS
(COMPLEMENTARY METAL-OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR)
A computer chip that allows many components to be packed together in a very small area. CMOS uses a very small
electric current, thereby generating very little heat, making it suitable for very-large-scale integration (VLSI). CMOS
are nonvolatile, meaning they retain their information even after the power is switched off. In a few words CMOS is a
digital logic family that is characterized by high density, low-to-medium power, and medium-to-high speeds.
DEVICE DRIVER
Software that tells the computer how to connect to a peripheral device, for instance a printer. It acts as an interface
between the operating system and the hardware attached to a computer, to allow applications to communicate in an
orderly fashion.
DIP
(DUAL IN-LINE PACKAGE)
A method of packaging semiconductor chips that was omnipresent until the 1980s. Since then, it is being replaced
with small outline packages for devices with low or medium pin counts and pin grid arrays or plastic quad flatpack for
devices with high pin counts.
DMA
(DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS)
A method of transferring blocks of data directly between a masse-storage device and memory, with no intervention
from the CPU. To transfer data from a non-storage devices (terminals) to a destination (memory), the CPU must
intervene in the transfer of each byte. The DMA interface is typically incorporated into the device controller.
Содержание TEK-AT4L Plus
Страница 7: ...PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW 2 ONBOARD SUBSYSTEMS...
Страница 9: ...Product Overview 1 2 TEK AT4LPLUS Block Diagram...
Страница 26: ...Installing Devices 6 3 CONNECTOR LOCATION...
Страница 35: ...Setting Jumpers 8 3 JUMPER LOCATIONS...
Страница 36: ...Setting Jumpers 8 5 TABLE 8 1 Jumper Settings W1 W11...
Страница 37: ...Setting Jumpers 8 6 TABLE 8 2 Jumper Settings W12 W19 W26...
Страница 38: ...Setting Jumpers 8 7 TABLE 8 3 Jumper Settings W20 W25 SW1 SW2...
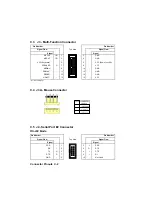
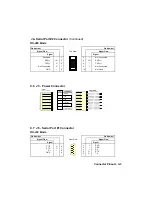
Страница 41: ...APPENDICES A PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS B BOARD DIAGRAMS C CONNECTOR PINOUTS...
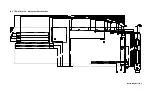
Страница 43: ...Board Diagrams B 1 B 1 TEK AT4LPLUS Assembly Diagram Top View...
Страница 44: ...Board Diagrams B 3 B 2 TEK AT4LPLUS Mounting Holes...
Страница 45: ...Board Diagrams B 5 B 3 TEK AT4LPLUS Mechanical Specifications...