Handbook for the TRIUS PRO-825C Issue 1 September 2020
11
The visible grid encodes the colour information within the image data and will now
be used to decode the red, green and blue image planes into a colour picture. To do
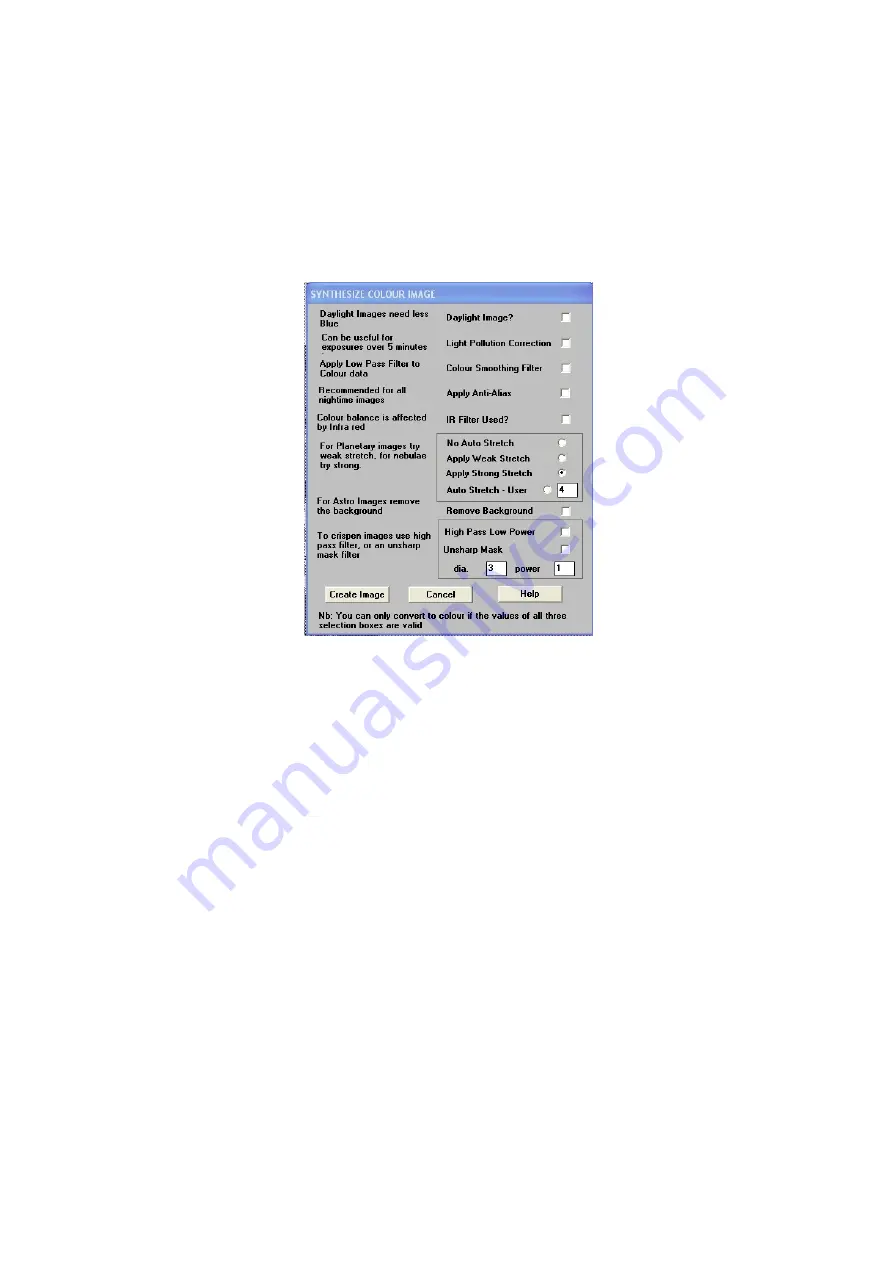
this, open the ‘Colour’ header tag where you will see the ‘Synthesize colour image’
option. Click on this to open the colour synthesis control panel.
The synthesis control panel contains several options for correcting colour bias and
noise.
1)
Daylight Image?
– If an unfiltered lens is used, the infra-red content of the
light will tend to produce a Green – Blue shift in the balance. A partial
correction of this bias is provided by selecting this option, but the best
option is to use an infra-red blocking filter when taking daylight shots (see 5
below).
2)
Light Pollution Correction:
- This option is for deep sky colour images, where
a strong colour bias is often present in the sky background. This option
attempts to return the background colour to a neutral grey.
3)
Colour Smoothing Filter:
- Applies a low pass filter to the colour data to
smooth out colour noise.
4)
Apply Anti
-
Alias:
- Runs a special filter over the colour data to remove
coloured artefacts around sharp edges. This is especially useful for cleaning
up erratically coloured star images.
5)
IR Filter Used? –
Sets the colour balance to allow for the loss of infra-red
content when using an IR blocking filter.
6)
Stretching: -
A selection of contrast-boosting options which are preset for
various subjects.


























