815_58300000003806_ara_en_e.doc – 30.01.12
Seite 30 von 67
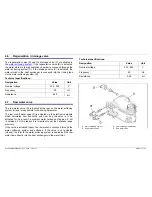
4.20 Water inlet with heat exchanger
When the filling valve has been opened, the water flows towards the
integrated inlet via the free flow channel and into the water softening
system and as soft water into the heat exchanger. When the
regeneration chamber has filled up, the water flows into the restricting
funnel of the level sensor via the overflow channel. The pressure
build-up in the pressure chamber causes the level switch to open the
heat exchanger drainage valve. The electronics measure the time
between the opening command of the filling valve and the closing of
the level switch (f1). The additional filling time of the filling valve is
calculated from this time.
The circulation pump is switched on time-delayed, the drainage valve
remains open until the heat exchanger has emptied completely.
The water volume of completed rinse cycles is recorded by the
electronics counter which determines when the water softener
requires regeneration.
Before each regeneration step the electronics check whether the
capacity of the water softener is adequate for a complete "Normal
Programme Sequence". If not, regeneration starts.
The water softening system is regenerated and rinsed through during
the wash cycle. The regeneration valve on the water softening system
is opened for this purpose. The stored volume of water flows into the
salt dispenser via the valve, absorbs salt and flows as saline solution
through the water softening system into the heat exchanger. Rinsing
takes place in three stages, each with one calculated volume of water.
A Free flow line
J Float in the base pan
B Leakage
water
K Salt
dispenser
C Overflow
channel
L Ion
exchanger
D Heat exchanger
M Heat exchanger drainage valve
E Pressure switch, level f1
N Regeneration valve
F Switch
lever
O Water
inlet
G Safety pressure switch
P Regeneration chamber
H Air chamber level
Q Drainage hose ventilation valve
I To the pump sump