33
Rated
maximum voltage
Rated power-frequency
withstand
Field-test voltage
kV (rms)
kV (rms)
kV (rms)
kV dc
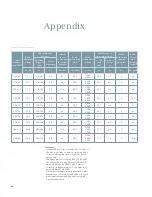
15.5
50
37.5
53
27.6
60
45
64
38.0
80
60
85
Table 3: High-potential test voltages
Note:
The dc test voltage is given as a
reference only. It represents values believed
to be appropriate and approximately
equivalent to the corresponding power-
frequency withstand test values specified for
each voltage rating. The presence of this
column in no way implies any requirement for
a dc withstand test on ac equipment or that a
dc withstand test represents an acceptable
alternative to ac withstand tests. When
performing dc tests, the voltage should be
raised to the test value in discrete steps and
held for a period of one minute.
Note: Do not use dc high-potential testers
incorporating half-wave rectification. Such
devices produce high peak voltages.
These high voltages will produce X-ray
radiation. Such devices also show erroneous
readings of leakage current when testing
vacuum circuit breakers.
Field dielectric tests are recommended
when new units are installed, or after
major field modifications. The equipment
should be put in good condition prior to
the field test. It is not expected that
equipment shall be subjected to these
tests after it has been stored for long
periods of time or has accumulated a large
amount of dust, moisture or other
contaminants without being first restored
to good condition.
A dielectric test on secondary and control
circuits should be made for one minute at
1,125 volts ac or 1,590 volts dc. The
above voltages are in accordance with
NEMA Standards.
Note:
Certain control devices, such as motors
and motor circuits, should be tested at 675
volts ac. Electronic devices should be tested
at the voltages specified in the instruction
manual for the electronic device.
3. Energize the control circuits. For
magnetic-actuator operators, the LEDs
show capacitor charging status.
4. Close the circuit breaker electrically
(locally and remotely as applicable) and
verify the circuit breaker shows CLOSED
and remains closed by checking the main
contact status indicator. Note that the
capacitors will recharge for magnetic-
actuator operators.
5. Trip the circuit breaker electrically (locally
and remotely as applicable).
6. Trip the circuit breaker by passing
sufficient current (or voltage if applicable)
through the coils of protective relays.
7. Repeat the close and trip operations
several times to assure proper operation.
8. Check the tripping and closing times from
coil energization to contact part or
contact make.
Содержание SDV7
Страница 54: ...54 Table 16 Remarks ...
Страница 55: ...55 Table 16 Remarks continued ...