General safety instructions
2.2 Safety Integrity Level (SIL)
Functional safety for SITRANS P, series DS III PROFIsafe
Product information, 07/2006, A5E00849297-01
2-3
The achievable SIL is determined by the following safety characteristics:
•
Average probability of dangerous failure of a safety function in case of demand (PFD
AVG
)
•
Hardware fault tolerance (HFT)
•
Safe failure fractions (SFF)
Description
The following table shows the dependency of the SIL on the "average probability of
dangerous failures of a safety function of the entire safety-instrumented system" (PFD
AVG
)
The table deals with "Low demand mode", i.e. the safety function is required a maximum of
once per year on average.
Table 2-1
Safety Integrity Level
SIL
PFD
AVG
4
≥ 10
-5
...< 10
-4
3
≥ 10
-4
...< 10
-3
2
≥ 10
-3
...< 10
-2
1
≥ 10
-2
...< 10
-1
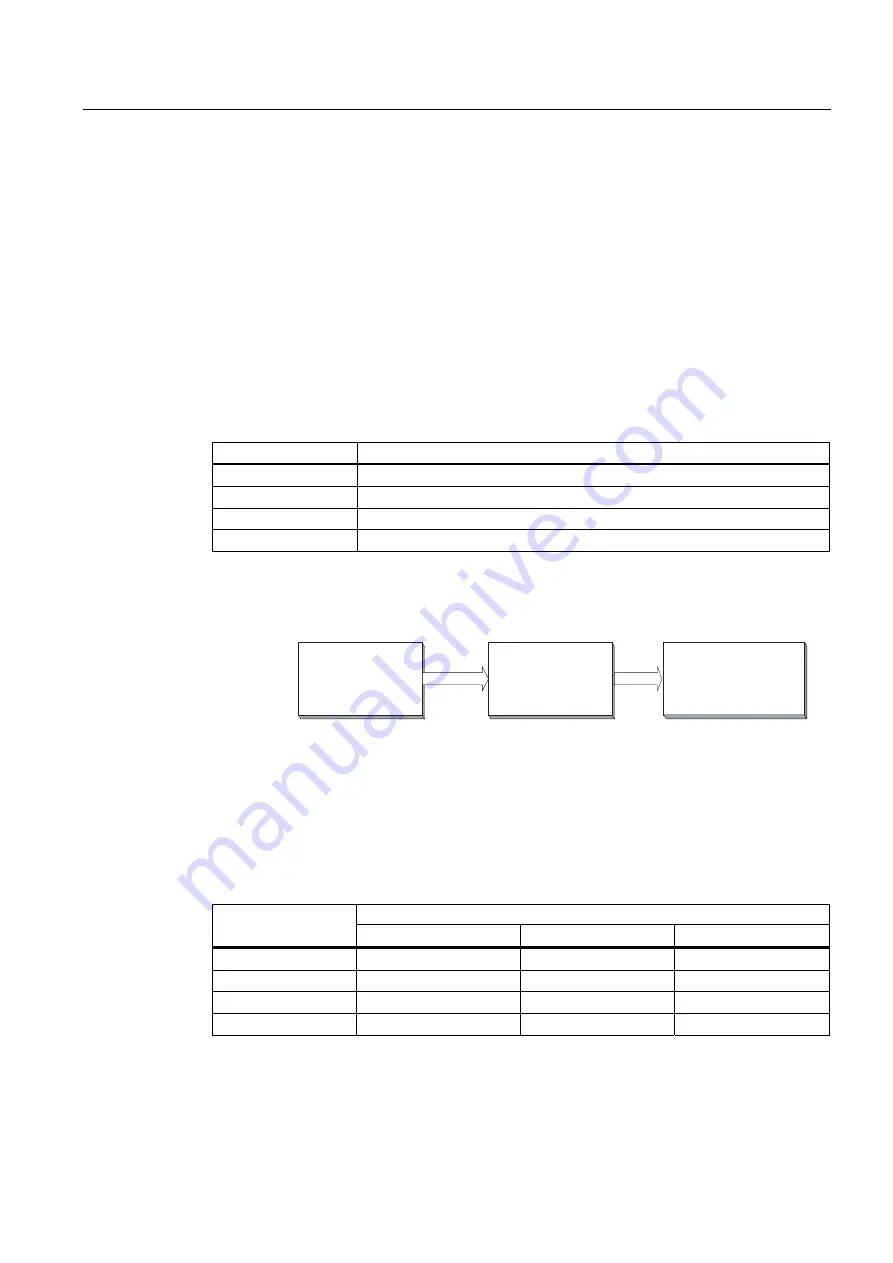
The "average probability of dangerous failures of the entire safety-instrumented system"
(PFD
AVG
) is normally split between the three sub-systems in the following figure.
6HQVRU
HJSUHVVXUH
WHPSHUDWXUHHWF
&RQWUROV\VWHP
RUORJLFXQLW
HJ
3/&
3)'
$9*
FRPSRQHQW
)LQDOFRQWUROOLQJ
HOHPHQW
HJYDOYHZLWKDFWXDWRU
DQGSRVLWLRQHU
Figure 2-2
Example of PFD distribution
The following table shows the achievable Safety Integrity Level (SIL) for the entire safety-
instrumented system for type B subsystems depending on the safe failure fraction (SFF) and
the hardware fault tolerance (HFT). Type B subsystems include analog transmitters and
shut-off valves without complex components, e.g. microprocessors (also see IEC 61508,
Section 2).
HFT
SFF
0
1 (0)
1)
2 (1)
1)
< 60 %
Not permissible
SIL 1
SIL 2
60 to 90 %
SIL 1
SIL 2
SIL 3
90 to 99 %
SIL 2
SIL 3
SIL 4
> 99 %
SIL 3
SIL 4
SIL 4
1)
As per IEC 61511-1, Section 11.4.4