8
TB MRD1-G 11.01 E
4
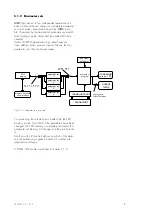
Working principle
In this chapter the individual functions and working
principle of the
MRD1
are described.
4.1
Protective functions
4.1.1
Generator differential protection
Term
Explanation
ID
Bias current
This is the current passing through the generator from the starpoint side to the grid
side. This current is representing the normal load.
Id
Differential current
The difference between grid side current and star point side current of one wind-
ing.
Ia
Pickup current
If the differential current exceeds the pickup current, the relay trips.
Fault current due to
operational condi-
tions
This kind of fault current is the component of the measured differential current
which, however, is not caused by a fault of the object to be protected but is of
systematic nature
Stabilization
Under this heading all measures are compiled which stabilize the differential relay
against nuisance tripping. Stabilizing always means the pickup current is raised
and by this the differential relay becomes more intensitive, but is never completely
blocked.
I
S
Stabilizing current
This current develops from the bias current and represents the extent of stabilizing
measures necessary as result of the fundamental analysis. Parameters of the
pickup characteristic can be set.
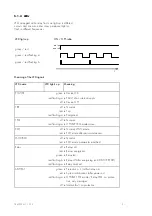
m
Harmonic stabilizing
factor
This factor, derived from the analysis of the harmonic frequency, is apart from I
S
the second stabilizing factor and in case of rush and saturation by following a
special characteristic makes the differential relay stable against tripping errors.
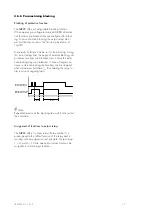
d[Id] Characteristic Offset The characteristic curve is raised up by the value d[Id] immediately after a har-
monic stabilization factor “m” is measured to be greater than zero. This is to give
a basic stabilization after detection of inrush or ct-saturation during external fault
by means of harmonic measurement.
Pickup characteristic This characteristic defines the stabilizing current dependence on the pickup current
Table 1: Term definitions