3. Installation
the MIC-Gain value to more than half of ist maximum, it is recommended to increase the
PSKAmpl
value. This, for example, can be done by entering <ESC>
FSKA
200
<RETURN>.
If no MIC-Gain potentiometer is available, the proper PSK amplitude-setting has to be
evaluated with only using the
PSKAmpl
command.
After the PSK amplitude is carefully adjusted, the MIC-Gain setting at the transceiver should
not be touched any more, otherwise it could be difficult to achieve the desired output level
for non-PSK modes.
To adjust the output level for non-PSK modes (FSK, CW, PACTOR-I, AMTOR, RTTY) only
the
FSKAmpl
command should be used now. Entering
U
1
<RETURN> starts the Unproto
mode 1 (=100Bd FSK). Now you have the chance to adjust the output value using the
FSKAmpl
command e.g. <ESC>
FSKA
100 <RETURN>
. Same as before, during this
procedure, be careful not to exceed the ALC limit.
To prevent damage from the transceiver at continuous operation, we recommend to limit the
FSK output level to half of the maximum possible, that means 50 W if the transceiver is made
for 100 W at max.
3.6
Transceiver Remote Control
The
SCS
PTC-IIIusb is equipped with a connector for controlling many common modern
amateur radio transceivers. Virtually all newer transceivers from KENWOOD, ICOM,
YAESU, SGC and R&S allow remote controlling of various functions via a serial interface.
Depending on type and manufacturer, almost all the transceiver parameters can be read out and
changed. For example frequency, filter, operating mode and much more can be controlled.
With radio equipment that is digitally controlled, the list of functions is almost unlimited.
The PTC-IIIusb uses this features mainly to set and readout the frequency of the transceiver.
You find more about the transceiver remote control in chapter TRX in the main manual.
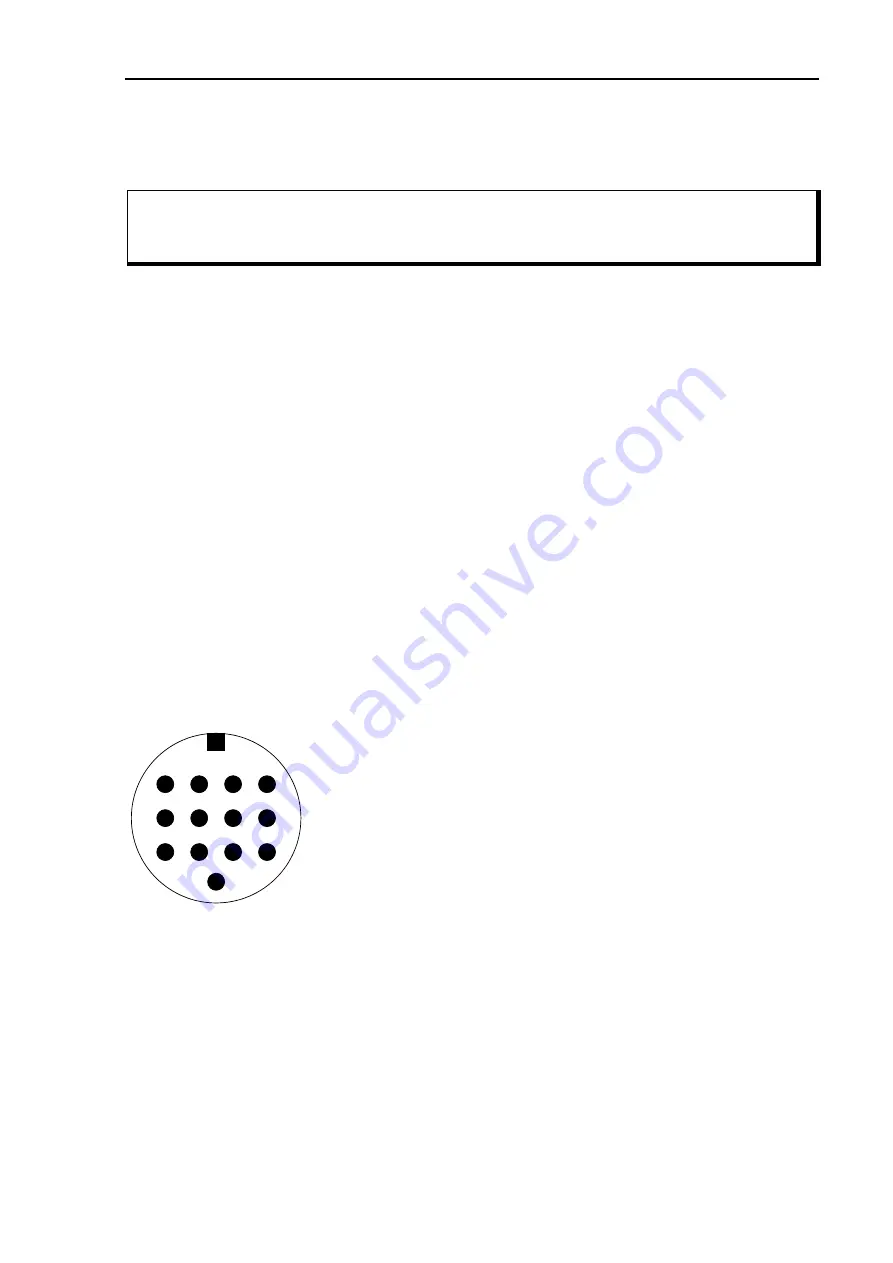
The 13 pin DIN Remote-control socket is connected as follows.
Seen from the back of the PTC-IIIusb
:
Pin 1:
RxD TTL.
Pin 2:
RTS V24.
Pin 3:
TXD V24.
Pin 4:
CTS V24.
Pin 5:
CTS TTL.
Pin 6:
ICOM.
Pin 7:
Not connected.
Pin 8:
RxD V24.
Pin 9:
TxD TTL.
Pin 10:
RTS TTL.
Pin 11:
Not connected.
Pin 12:
Not connected.
Pin 13:
GND.
2
4
3
5
6
7
8
9
13
1
10
11
12
Figure 4: Transceiver remote-control
TxD TTL
Transmit data from the PTC to the transceiver. TTL level!
RxD TTL
Receive data from the transceiver to the PTC. TTL level!
CTS TTL
Handshake signal from the transceiver to the PTC. TTL level!
RTS TTL
Handshake signal from the PTC to the transceiver. TTL level!
43