Page 11
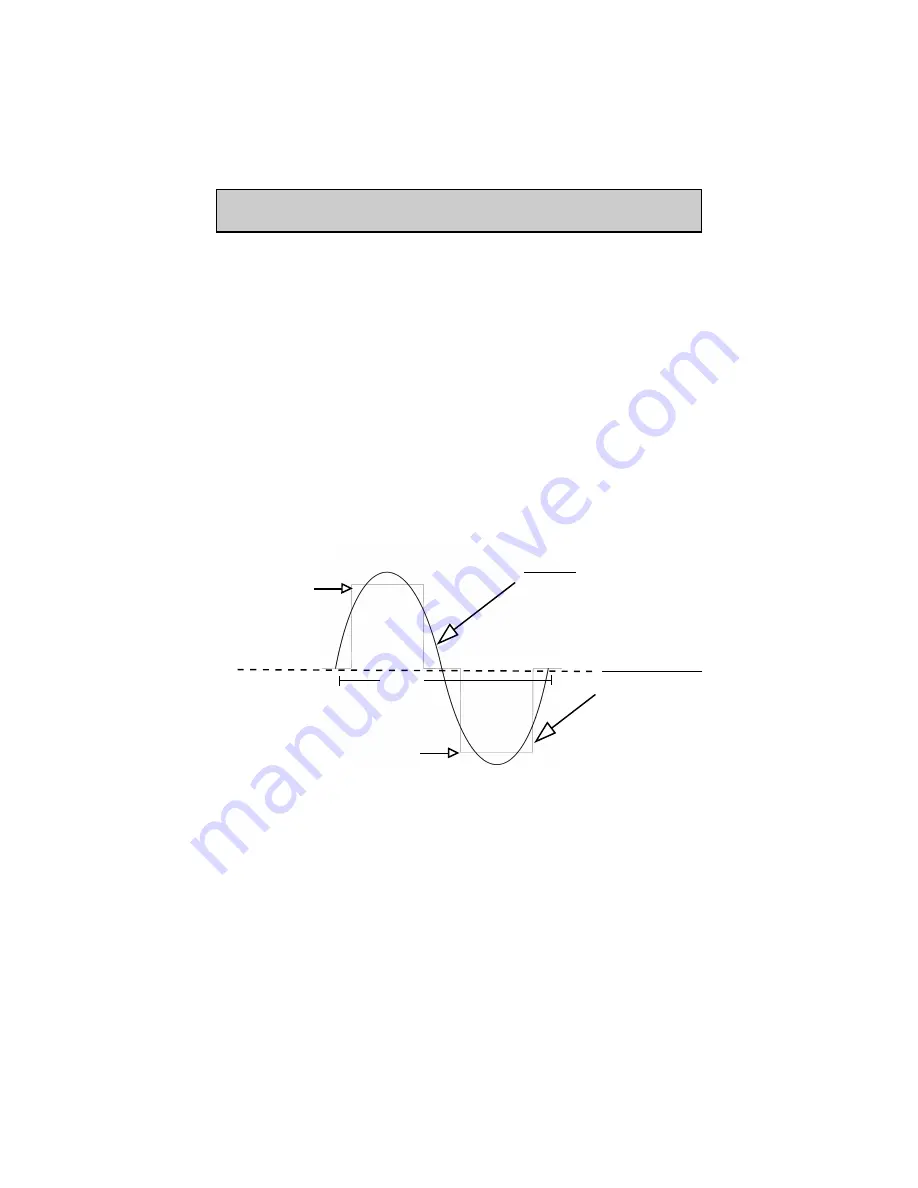
0V
-155 to -170V, Peak
Sinewave: Smoothly increases to
its peak and smoothly decreases.
It crosses 0 V immediately.
Has RMS value of 120V
Modified Sinewave:
Shoots straight up,
levels off at peak &
drops straight down.
Also, it sits at 0 V for
some time.
Has RMS value of
120V
1
/60
sec
+155 to 170V, Peak
+170V, Peak
-170V, Peak
(not to scale)
The inverter converts the 24 V (nominal) DC voltage of the battery to 120 V, 60 Hz. AC
voltage.
The voltage conversion takes place in two stages. In the first stage, the 24 V (nominal)
DC voltage of the battery is converted to high voltage DC (155 V to 170 V) using high
frequency switching and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technique. In the second stage,
the high voltage DC is converted to 120 V, 60 Hz. modified sine-wave AC (
Note
: 120 V
is the RMS value of the AC voltage. The peak value of the AC voltage will be equal to
the value of the above high voltage. See the diagram below)
The output wave form of the inverter is a modified sine wave (see the diagram given
below)
.
In a sine wave, the voltage rises and falls smoothly with a smoothly changing
phase angle and also changes its polarity instantly when it crosses 0 Volts. In a modified
sine wave, the voltage rises and falls abruptly, the phase angle also changes abruptly and
it sits at 0 Volts for some time before changing its polarity.
Measuring modified sine-wave voltage with a voltmeter
The modified sine-wave AC produced by the inverter has an RMS (Root Mean Square)
value of 120 V. A general purpose AC voltmeter is designed to accurately measure the
RMS value of a normal sine-wave and not a modified sine-wave. If this voltmeter is used
to read the AC voltage of a modified sine-wave, it will indicate a lower value (96 V to
104 V). For accurately measuring the voltage of a modified sine wave, use a voltmeter
which is designed to measure “true RMS values” like Fluke 87, Fluke 8060A etc
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION













































