4
VENTED APPLICATIONS (Additional Requirements)
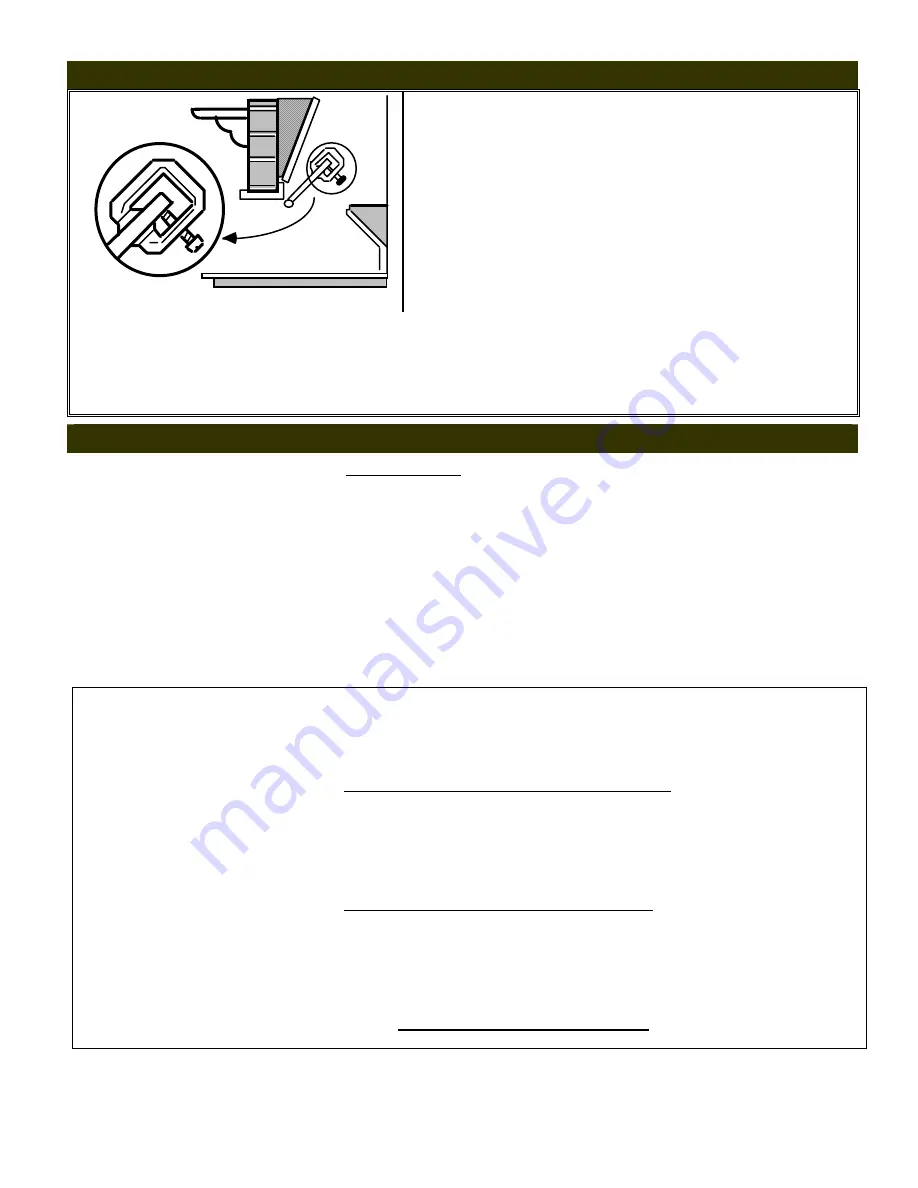
Damper Stop
Clamp
Damper
Chimney
Flue
General Information:
1. The minimum permanent free opening of the fireplace
chimney or chimney damper must be at least
29
sq. inches
based upon a minimum chimney height of at least 10 feet.
2. Solid fuels shall not be burned in a masonry or UL 127 factory
builtfireplace where a CHILLBUSTER is installed.
Damper Clamp:
1. The chimney damper must be fixed in a manner to maintain
permanent free opening as (outlined in item above) at all
times.
To accomplish this, install the damper clamp (provided) on the
edge of the damper blade to prevent its closing, or drill holes
in the damper
.
Manufactured Home (U.S. Only) or Mobile Home Installation:
1. Installation in a manufactured home (U.S. only), or mobile home installation must conform with the Manufactured
Home Construction and Safety Standard, Title 24 CFR, Part 3280, in the U.S., or with the Standard CAN/CSA Z240
MH, Mobile Housing, in Canada, or when such a standard is not applicable, ANSI/NCSBCS A225.1/NFPA 501A,
Mobile Home Installation Standard. Accessory attaching bracket
MH-1
is available from Rasmussen and is required
to permanently attach the burner /grate assembly to the solid fuel burning fireplace.
VENT-FREE APPLICATIONS (Additional Requirements)
1. Do not use this CHILLBUSTER as a Vent Free Heater in sleeping quarters, bathrooms or recreational vehicles.
2. When operated as a
VENT FREE
heater, the minimum clearances from the fireplace opening to combustible
materials must be maintained as outlined in section
"CLEARANCES TO COMBUSTIBLES"
(page 6).
3. The installation and the provision for combustion and ventilation air must conform with the National Fuel Gas Code
ANSI Z223.1 latest edition.
PROVISIONS FOR ADEQUATE COMBUSTION AND VENTILATION AIR
Confined Or Unconfined Space Determination
The National Fuel Gas Code defines a confined space as a space whose volume is less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000
Btu per hour (4.8m
3
per kW) of the aggregate input rating of all appliances installed in that space and an unconfined
space as a space whose volume is not less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour (4.8m
3
per kW) of the aggregate
input rating of all appliances installed in that space. Rooms communicating directly with the space in which the
appliances are installed, through openings not furnished with doors, are considered a part of the unconfined space.
Calculations To Determine Confined Or Unconfined Space:
1. Determine number of rooms (including adjoining rooms with doorless passageways or ventilation grates.)
Example:
Living room/dining room + Kitchen
2. Determine the
Total Volume of the Space
(width x length x height).
Example:
Living room/dining room 14' x 20' x 8' = 2240 cu ft
Kitchen
8' x 12' x 8' = 768 cu ft
Total Volume of Space
3008 cu ft
3. Divide the total space volume by 50 cuft to determine the
Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr.
Example:
3008 cu ft ÷ 50 = 60.160 x 1000 = 60,160
Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr = 60,160 Btu/Hr.
4. Add the rated (Btu/hr) of all fuel burning appliances in the "space" to determine
Actual Btu/Hr Used
.
Example:
Vent free gas log heater 40,000 Btu/Hr
Gas
water
heater
32,000
Btu/Hr
Actual Btu/Hr Used
72,000 Btu/Hr
Note: Do not include direct vent gas appliances.
5.
Compare
Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr
against
Actual Btu/hr Used
.
•If
Actual Btu/Hr Used
is
greater
than
Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr
then space is
CONFINED
.
•If
the
Actual Btu/Hr Used
is
less
than
Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr
then space is
UNCONFINED
.
60,160 Btu/Hr = Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr
-
72,000 Btu/Hr = Actual Btu/Hr Used
-
11,840 Btu/Hr = Excess Non-Supportable Btu/Hr
In the example, because the
Actual Btu/Hr Used
exceeds the
Maximum Supportable Btu/hr
the space would be
considered a
Confined Space
requiring you to either increase the
Maximum Supportable Btu/Hr, decrease
the
Actual Btu/Hr Used or operate as a Vented Appliance
(see page 3).

































